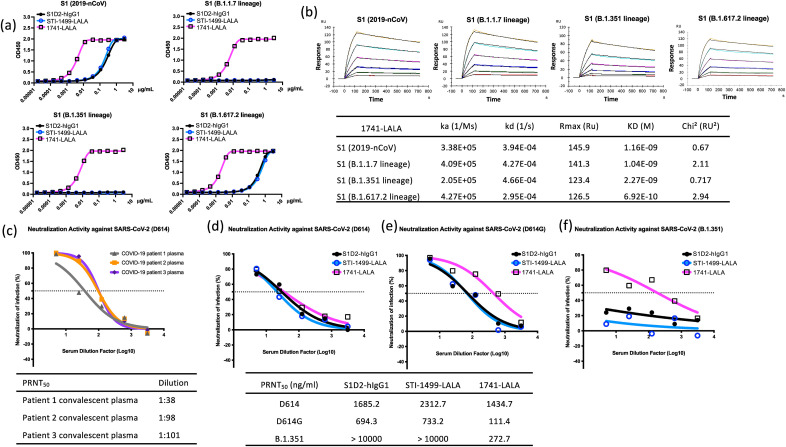
Fig. 1.
Kinetic interaction between anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike mAbs and variant spike protein, neutralization abilities of convalescent plasma and anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike mAbs against SARS-CoV-2 strains B.1.351, D614, and D614G. (a) Binding responses of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S protein mAbs, S1D2-hIgG1, STI-1499-LALA and 1741-LALA to the S1 fragment of the S protein from SARS-CoV-2 variants, including 2019-nCoV, B.1.1.7 (HV69-70 deletion, Y144 deletion, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H)-, B.1.351 (K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G)-, and B.1.617.2 (T19R, G142D, E156G, 157–158 deletion, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R)- lineage. (b) Panels indicate the association and dissociation of 1741-LALA at various concentrations binding to S1 of 2019-nCoV, B.1.1.7, B.1.351 and B.1.617.2 lineage. The table shows the association rate (ka), dissociation rate (kd), and dissociation constant (KD). Neutralization titers of (c) convalescent plasma from three different COVID-19 patients against SARS-CoV-2 D614 and PRNT50 curves of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike mAbs against (d) D614 (e) D614G, and (f) B.1.351. Tables indicate the titers of each plasma sample or mAb concentrations in neutralizing 50% of input virus.