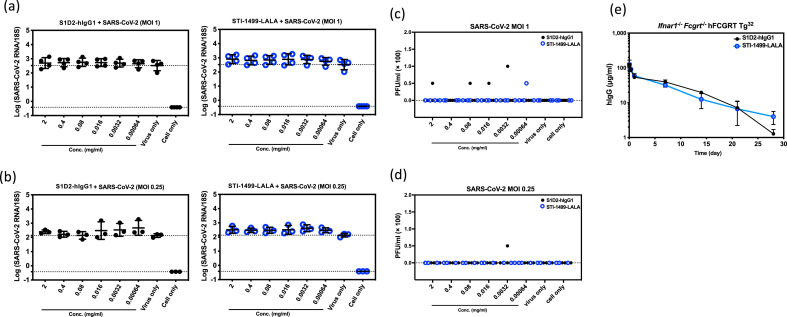
Fig. 3.
Negligible enhancement of SARS-CoV-2 infection with anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike mAbs on primary human monocyte derived macrophages. Serial diluted anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike mAbs S1D2-hIgG1 and STI-1499-LALA were incubated with SARS-CoV-2 at MOI 1 (a, c) or MOI 0.25 (b, d) for 1 h prior to inoculation onto macrophages. Viral RNA (a, b) and infectious viral particles (c, d) at 2 days post infection were evaluated. Data are presented as the mean with SD (n = 3–4). Each data point represents the average of a duplicate from each testing condition with macrophages derived from different donors. The differences of ADE conditions between various concentration of mAbs and virus only group were tested with one-way ANOVA. (e) Mean serum human IgG concentration-time profiles of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike mAbs S1D2-hIgG1 and STI-1499-LALA in Ifnar1−/−Fcgrt−/− hFCGRT Tg32 mice. Each data point indicates a mean serum concentration from 3 to 4 mice. Error bars show the SD from mean. Mann-Whitney test was used to test the difference of serum hIgG concentration between S1D2-hIgG1 and STI-1499-LALA harvested at various time points.