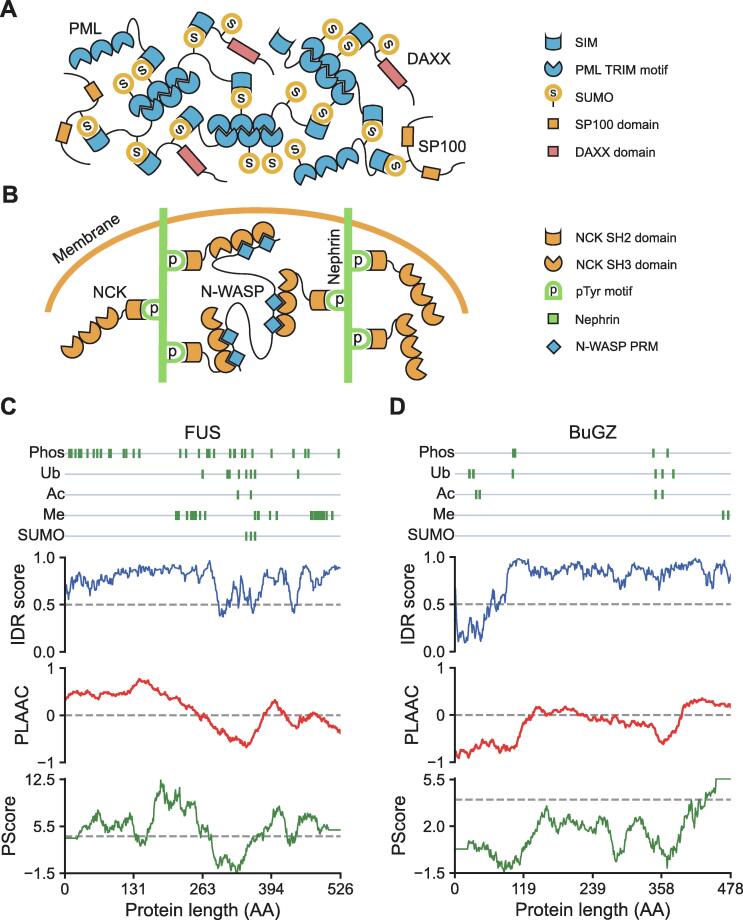
Figure 1.
Schematic view of multivalent interactions that promotephase separation
A. PML protein can not only self-assemble via interactions between its TRIMs but also interact via its SIM with SUMOs of itself and other proteins, such as DAXX and SP100. B. Schematic view of nephrin–NCK–N-WASP system. The cytoplasmic tail of nephrin contains three pTyr sites, each of which can bind to an SH2 domain on NCK. The three SH3 domains on NCK can also bind to PRMs within N-WASP. C. Residue-wise plot of scaffold protein FUS. Information of PTM sites was collected from the PhosphoSitePlus database; IDR scores were predicted by IUPred for long disorder; the prion-like domain was identified with PLAAC score greater than zero; the pi-contact was identified with PScore greater than four, as indicated by dashed line. D. Residue-wise plot of scaffold protein BuGZ. PML, promyelocytic leukemia; TRIM, tripartite motif; SIM, SUMO-interacting motif; SUMO, small ubiquitin-like modifier; DAXX, death domain-associated protein; SP100, nuclear autoantigen Sp-100; NCK, non-catalytic region of tyrosine kinase; N-WASP, neuronal Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein; pTyr, tyrosine phosphorylation; SH, Src homology; PRM, proline-rich motif; FUS, fused in sarcoma; PTM, post-translational modification; IDR, intrinsically disordered region; BuGZ, BUB3-interacting and GLEBS motif-containing protein ZNF207; Phos, phosphorylation; Ub, ubiquitination; Ac, acetylation; Me, methylation; AA, amino acid.