Figure 6.
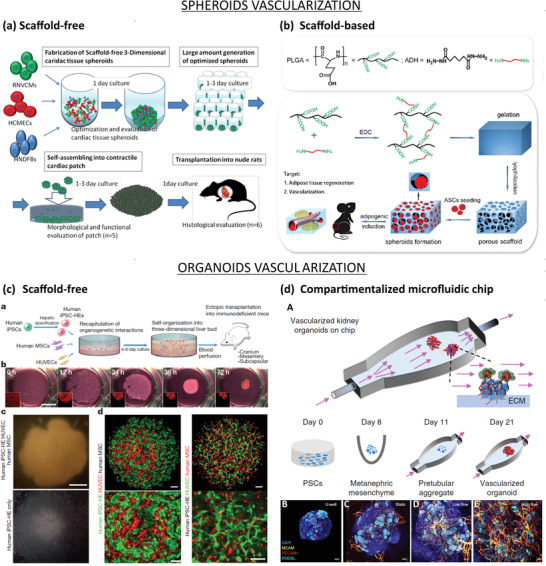
Vascularization approaches for spheroids (top) and organoids (bottom). a) Scaffold‐free approach to vascularize spheroids. RNVCMs, HCMECs, and hNDFs were cocultured at optimal cell ratios (70%:15%:15%) and plated into ultralow attachment 96 U‐well plates to form cardiac tissue spheroids. Then, the spheroids were collected and plated in low‐attachment dishes, allowing them to self‐organize into cardiac patch grafts under static conditions. Finally, the cardiac patch grafts were transplanted on the anterior wall of the left ventricle of arhythmic rats to induce spontaneous vascularization. Reproduced with permission.[ 148 ] Copyright 2016, Elsevier Inc. b) Scaffold‐based approach to vascularize spheroids. PLGA activated by 1‐ethyl‐3‐(3‐dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and crosslinked with adipic dihydrazide, followed by lyophilization forms porous hydrogel. Seeding of ASCs onto hydrophilic surface induced cell aggregations, which resulted in ASC‐spheroids. Then, the spheroids were transplanted in the dorsum of nude mice to induce spontaneous vascularization. Reproduced with permission.[ 147 ] Copyright 2017, Elsevier Inc. c) Scaffold‐free approach to vascularize organoids: a) Schematic representation of the paper's strategy: hiPSCs, hMSCs, and HUVECs cocultured on Matrigel to form liver organoids, which were transplanted into mice to induce spontaneous vascularization. b) Observation of cells in coculture overtime. Organoids formed within 72 h. c) Observation of hiPSC‐organoids (top panel) and conventional 2D cultures (bottom panel). Scale bar = 1 mm. d) Confocal images showing the presence of hiPSC‐derived hepatic endoderm cells (green) and HUVECs (red) inside liver organoids (left panel), or HUVECs (green) and hMSCs (red) inside hiPSC‐derived organoids. Scale bar = 100 µm. Adapted with permission.[ 117 ] Copyright 2013, Springer Nature. d) Compartmentalized microfluidic‐based hybrid strategy: A) Kidney organoids were cultured in ECM substrate housed inside a perfusable millifluidic chip, subjected to controlled fluidic shear stress. B–E) Confocal 3D observations showing vascular markers in whole‐mount organoids, cultured under static U‐well, static, low‐FSS, and high‐FSS conditions. Scale bars = 100 µm. Adapted with permission.[ 137 ] Copyright 2019, Springer Nature.
