Figure 1.
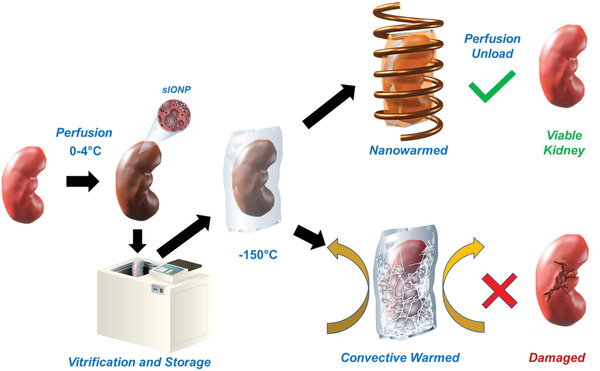
Schematic flow of kidney nanowarming. The kidney is hypothermically (0–4 °C) perfused with CPA (VS55) and sIONPs through the renal artery, then immersed in a cryobag containing VS55+sIONP and cooled rapidly to a vitrified state at −150 °C in a controlled rate freezer (CRF). During rewarming, convective warming in air or water‐bath will result in ice crystallization due to insufficient warming rates and/or cracking from thermomechanical gradients, thus damaging the kidney. In contrast, nanowarming of the kidney, using an RF magnetic field, results in rapid and uniform heating, minimizing cryopreservation damage that results in recovery similar to CPA load and unload only controls.
