Figure 4.
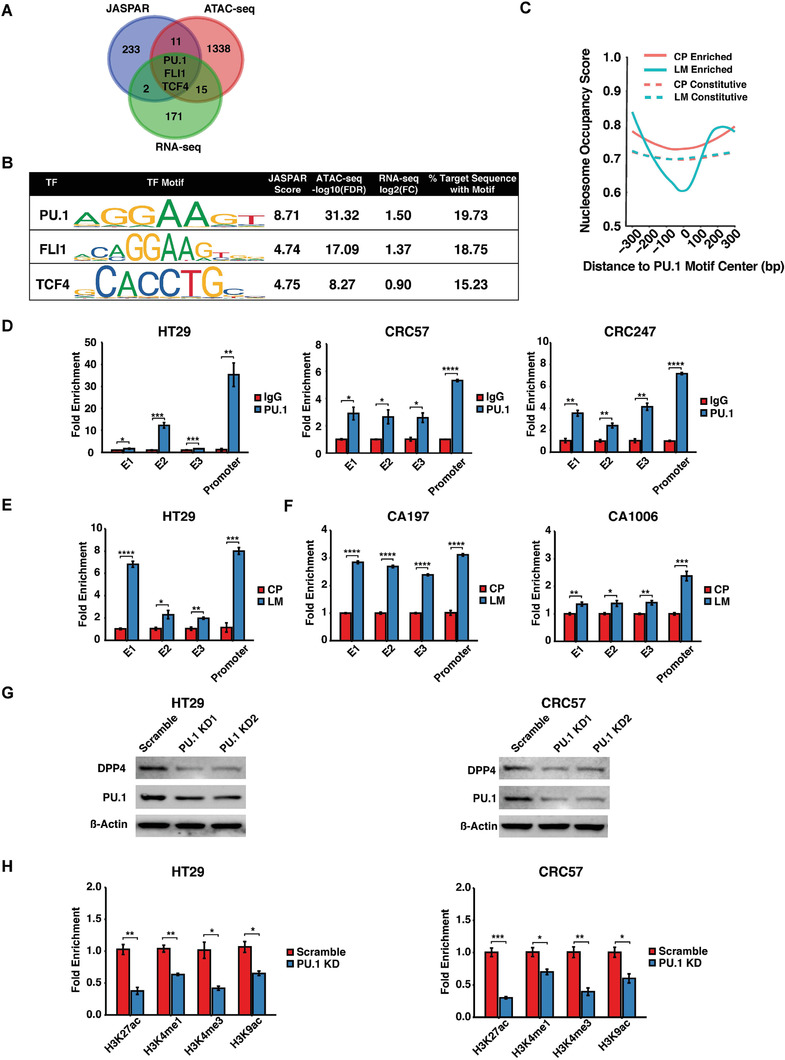
PU.1 upregulates DPP4 expression through remodeling DPP4‐associated chromatin. A) Integrated analysis of JASPAR, RNA‐seq, and ATAC‐seq revealing three potential DPP4 epigenetic regulators. B) Corresponding scores of the potential DPP4 regulators. C) Nucleosome occupancy analysis of enriched or constitutive peaks from liver metastases or primary CRC centered at PU.1 motif with 300 bp flanking window. D) ChIP‐qPCR showing PU.1 binding in DPP4 promoter and enhancer regions. E,F) ChIP‐qPCR showing PU.1 binding to DPP4 promoter and enhancers in HT29‐derived liver metastases versus primary tumors from E) CRC orthotopic‐model, and F) patient‐derived CRC organoids. G) Western blots showing DPP4 expression levels in HT29 or CRC57 carrying scrambled (control) or PU.1 knockdown (PU.1 KD1 or KD2) shRNAs constructs. H) ChIP‐qPCR showing relative H3K27ac, H3K4me1, H3K4me3, and H3K9ac enrichments in HT29 or CRC57 carrying scrambled (control) or PU.1 knockdown (PU.1 KD1) shRNA constructs. LM, liver metastases. CP, CRC primary tumor. E1, E2, and E3, enhancer 1, enhancer 2, and enhancer 3. Data represent the mean ± s.d. p‐values were calculated based on Student's t‐test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
