Figure 1. Weekly Vaccine Administration Rates for Included Pediatric Populations.
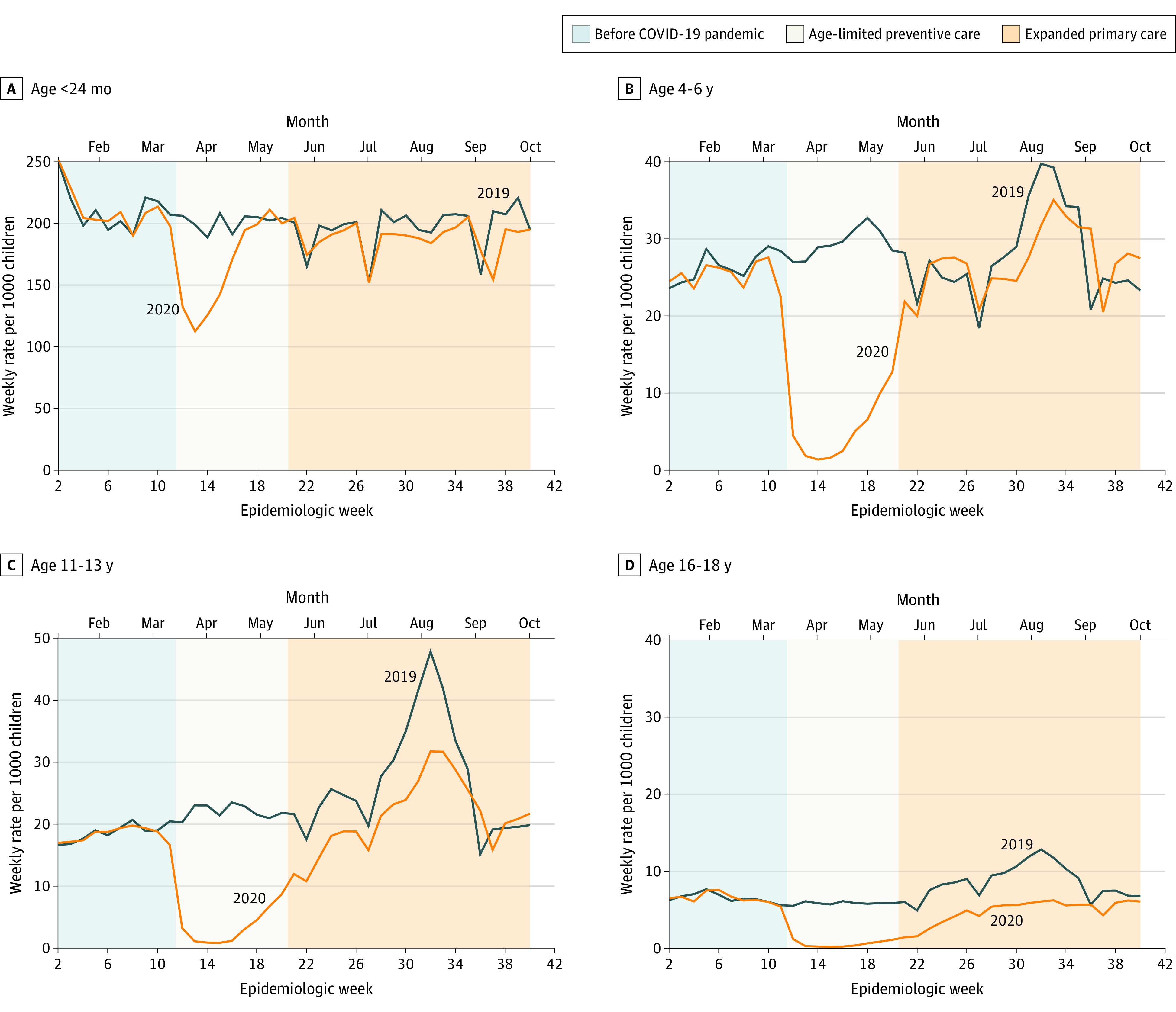
Data are from 8 US health systems in the Vaccine Safety Datalink and are organized by age group (<24 months, 4-6 years, 11-13 years, and 16-18 years) and period, 2019 and 2020. These ranges include data from January 6 through October 5, 2019, and January 5, 2020, through October 3, 2020. Vaccines varied by age group. In those younger than 24 months: hepatitis B; rotavirus; diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis; Haemophilus influenzae type B conjugate; pneumococcal conjugate, 13-valent; inactivated polio; measles, mumps, rubella; and varicella-zoster vaccines were standard. In children aged 4 to 6 years, measles, mumps, and rubella; varicella-zoster; diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis; and inactivated polio vaccines were standard. In children aged 11 to 13 years, human papillomavirus; tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis; and quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccines were standard. In those aged 16- to 18 years, human papillomavirus and quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccines were standard.
