Figure 2. Proportion of Individuals Up to Date for Routine Childhood Vaccines .
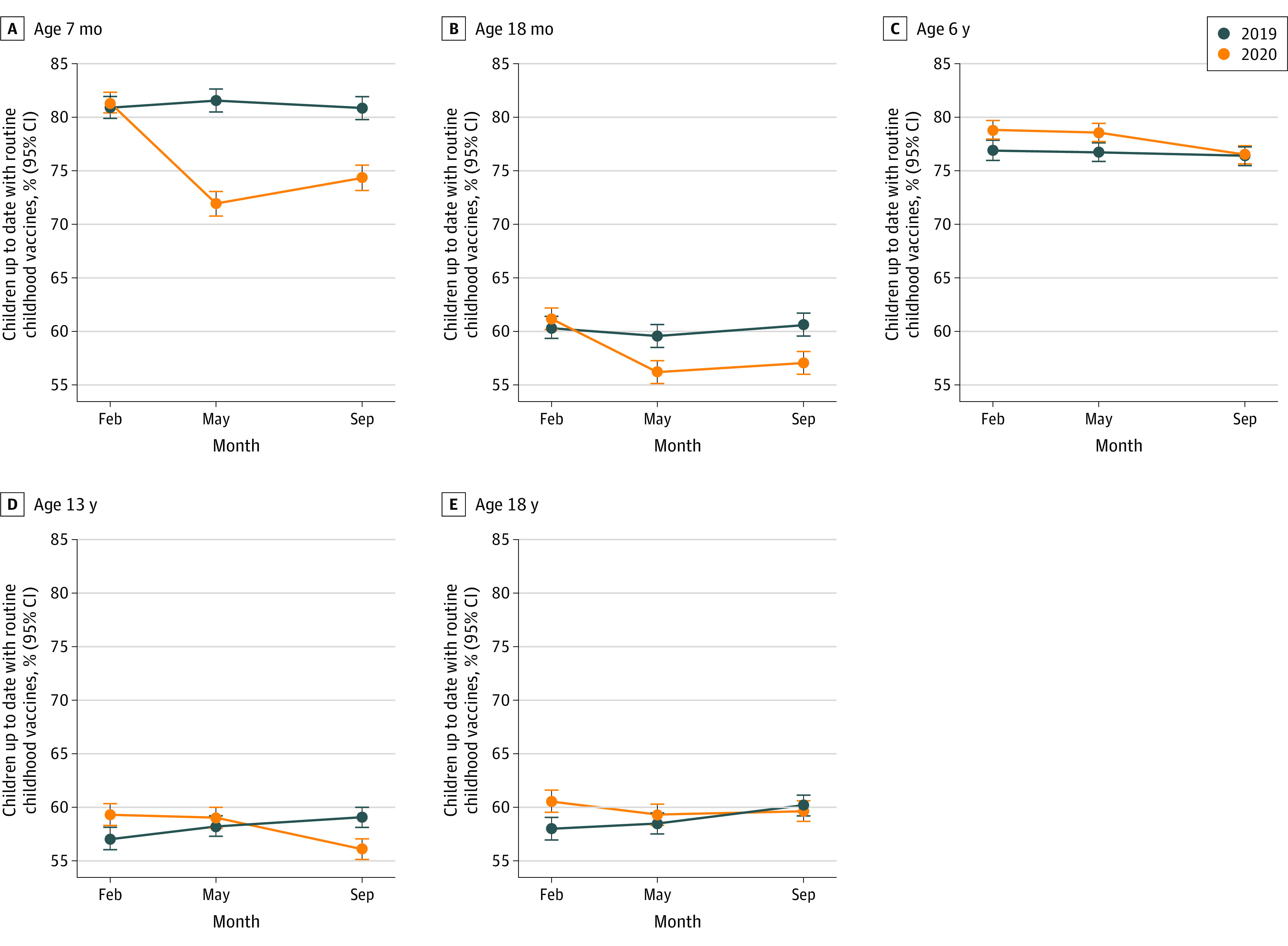
Data include 95% CIs. Data are from 8 Vaccine Safety Datalink health systems, among infants, children, and adolescents reaching specified ages in February, May, and September 2019 and 2020. Up-to-date definitions varied by age. At age 7 months, infants must have received 2 hepatitis B; 2 rotavirus; 3 diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis; 2 Haemophilus influenzae type B conjugate; 3 pneumococcal conjugate, 13-valent; and 2 inactivated polio vaccine doses. At age 18 months, children must have received 3 hepatitis B; 4 diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis; 3 H influenzae type B conjugate; 4 pneumococcal conjugate, 13-valent; 3 inactivated polio; 1 measles, mumps, and rubella; and 1 varicella-zoster virus vaccine doses. At age 6 years, they must be in receipt of 5 diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis; 4 inactivated polio; 2 measles, mumps, and rubella; and 2 varicella-zoster virus vaccine doses. At age 13 years, they must have received 2 human papillomavirus; 1 tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis; and 1 quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine doses. At age 18 years, they must have received 2 human papillomavirus; 1 tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis; and 2 quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine doses.
