Figure 1. GSDMD modulates clinical features of murine lupus.
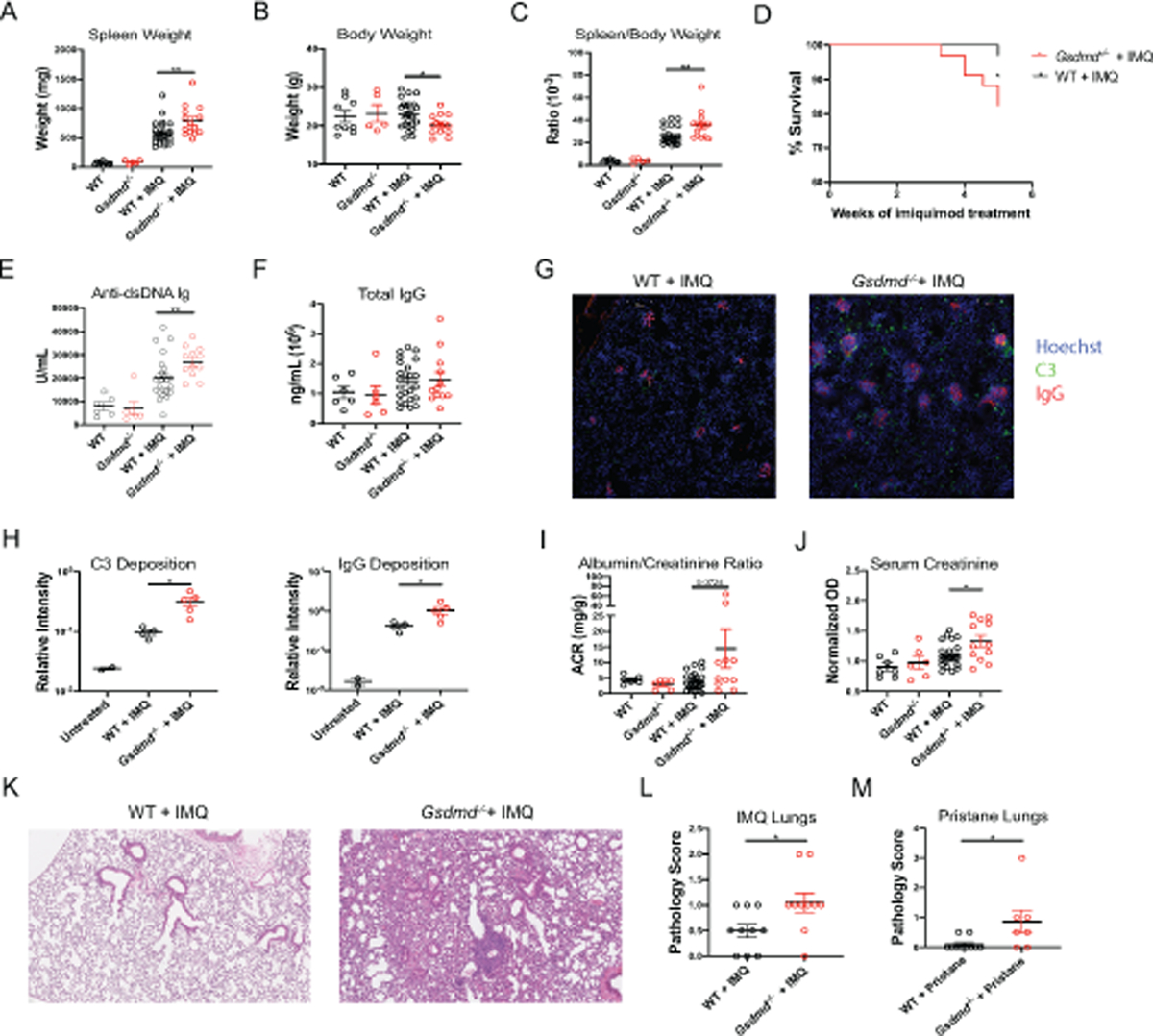
(A–C) Spleen weight, body weight, and spleen/body weight ratios of untreated and imiquimod-treated wild-type (WT) and Gsdmd−/− mice. (D) Survival curve of imiquimod-treated mice. (E, F) Serum anti-dsDNA and total IgG concentrations. (G–H) 10X images of frozen kidney sections stained for C3, IgG, and Hoescht and quantified using Fiji software. Images are representative of 4–5 mice. (I) Urine Albumin/Creatinine Ratio and (J) serum creatinine concentrations. (K–L) Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) lung sections from imiquimod-treated mice were analyzed for bronchial and alveolar inflammation. (M) FFPE lung sections from pristane-treated mice were analyzed for overall severity. (A–C), n=9 WT, 5 Gsdmd−/−, 24 WT + IMQ, 12 Gsdmd−/− + IMQ. (D), n=34 WT + IMQ, 30 Gsdmd−/− + IMQ. (E, F, J) n=6 WT, 5 Gsdmd−/−, 24 WT + IMQ, 12 Gsdmd−/− + IMQ. (K-L) n=10 WT + IMQ, 10 Gsdmd−/− + IMQ. (M) n=10 WT + IMQ, 7 Gsdmd−/− + IMQ. Dots indicate individual mice. Results represent mean ± SEM. Statistics were calculated by non-parametric Mann-Whitney test for all except (D), where Kaplan-Meier survival analyses was performed; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
