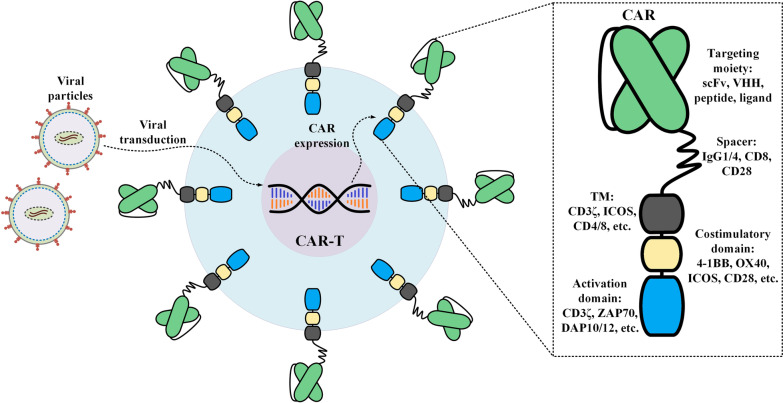
Fig. 1.
A detailed representation of a CAR molecule. Isolated T cells are transduced with viral particles and the gene fragment encoding the CAR constructs are integrated within their genome (as is in the case of CAR-T products approved for medical use in the US). This leads to the expression of the CAR molecules on the surface of the transduced T cells. In detail, a conventional CAR is composed of a targeting moiety followed by a spacer fragment, also known as a hinge, a transmembrane domain, a costimulatory domain, and an activation domain. So far, five generations of CARs have been devised by different investigational teams with different characteristics and components which have been comprehensively discussed elsewhere [36, 37]. CAR chimeric antigen receptor; ICOS the inducible T-cell co-stimulator; scFv single-chain variable fragment; TM transmembrane domain