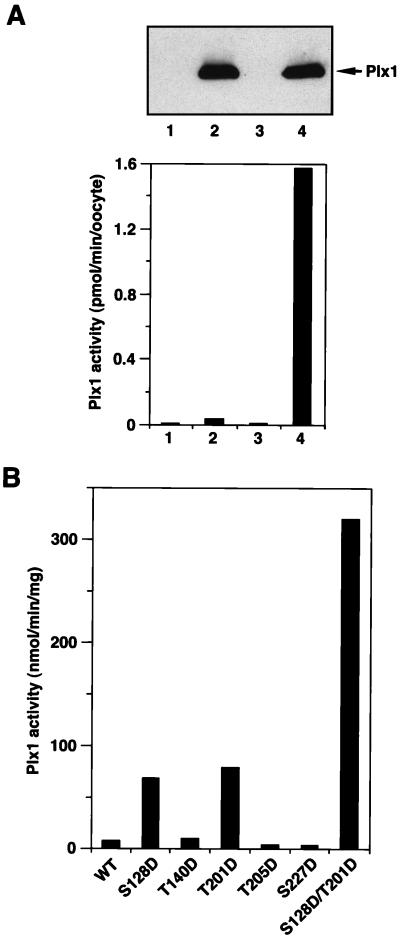
FIG. 2.
Protein kinase activity of various Plx1 mutants. (A) Wild-type Plx1 is not activated in the absence of progesterone treatment. Stage VI oocytes were microinjected with buffer or 40 ng of mRNA encoding FLAG-tagged WT Plx1, either treated or untreated with progesterone, and harvested 15 min after the progesterone-treated oocytes underwent GVBD. Extracts were prepared, and samples equivalent to one oocyte were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG M2 agarose beads and washed; the immunocomplexes were then assayed for phosphorylation of α-casein (lower panel) or immunoblotted with anti-Plx1 antibody (upper panel). Lane 1, stage VI oocytes, buffer injection; lane 2, stage VI oocytes, Plx1 mRNA injection; lane 3, GVBD oocytes, buffer injection; lane 4, GVBD oocytes, Plx1 mRNA injection. (B) Specific acidic mutations activate Plx1 in the absence of progesterone treatment. Stage VI oocytes were microinjected with 40 ng of mRNA encoding the various FLAG-tagged Plx1 mutants, as indicated, and harvested 3 h later. At this time the oocytes expressing mutant Plx1 were still in stage VI, based on the histone H1 kinase activity (data not shown). Extracts were prepared, and immunoprecipitates were assayed for phosphorylation of α-casein. The amount of Plx1 protein in the immunocomplexes was determined by immunoblotting, with purified recombinant Plx1 as a standard.