Figure 1 .
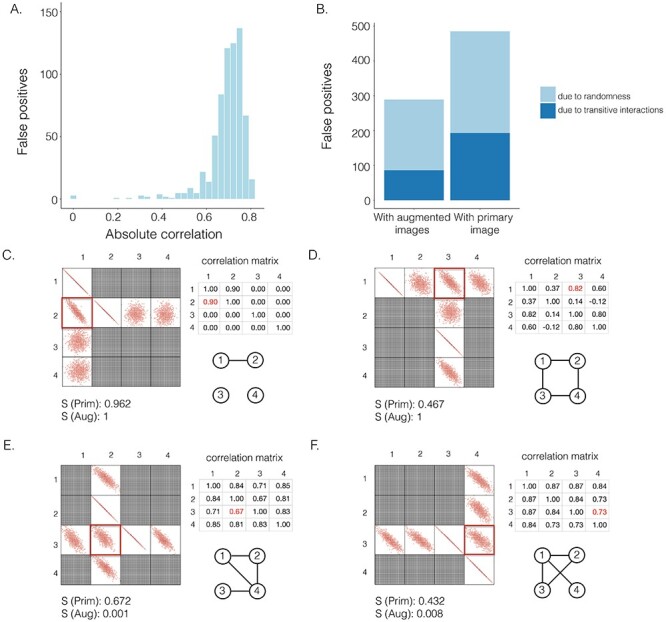
The effectiveness of neighbor images in reconstructing GRNs on the simulated data. A. The distribution of false positives from CNNC. B. The false positives of the two models with primary (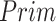 ) and augmented (
) and augmented (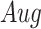 ) images as inputs due to randomness and transitive interactions. C and D. Two examples that demonstrate both of the models can correctly identify the direct interactions (C:
) images as inputs due to randomness and transitive interactions. C and D. Two examples that demonstrate both of the models can correctly identify the direct interactions (C: 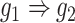 , D:
, D: 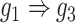 ). E and F. Two examples that demonstrate the model trained by augmented images can recognize and eliminate the false positives caused by the transitive edges (E:
). E and F. Two examples that demonstrate the model trained by augmented images can recognize and eliminate the false positives caused by the transitive edges (E: 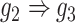 , F:
, F: 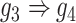 ).
). 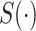 denotes the confidence scores from CNNC with primary (
denotes the confidence scores from CNNC with primary (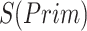 ) or augmented images (
) or augmented images (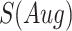 ) as inputs. The values in the correlation matrices are Pearson correlation coefficients for the gene pairs in the corresponding entries. The primary images are highlighted in the red squares.
) as inputs. The values in the correlation matrices are Pearson correlation coefficients for the gene pairs in the corresponding entries. The primary images are highlighted in the red squares.
