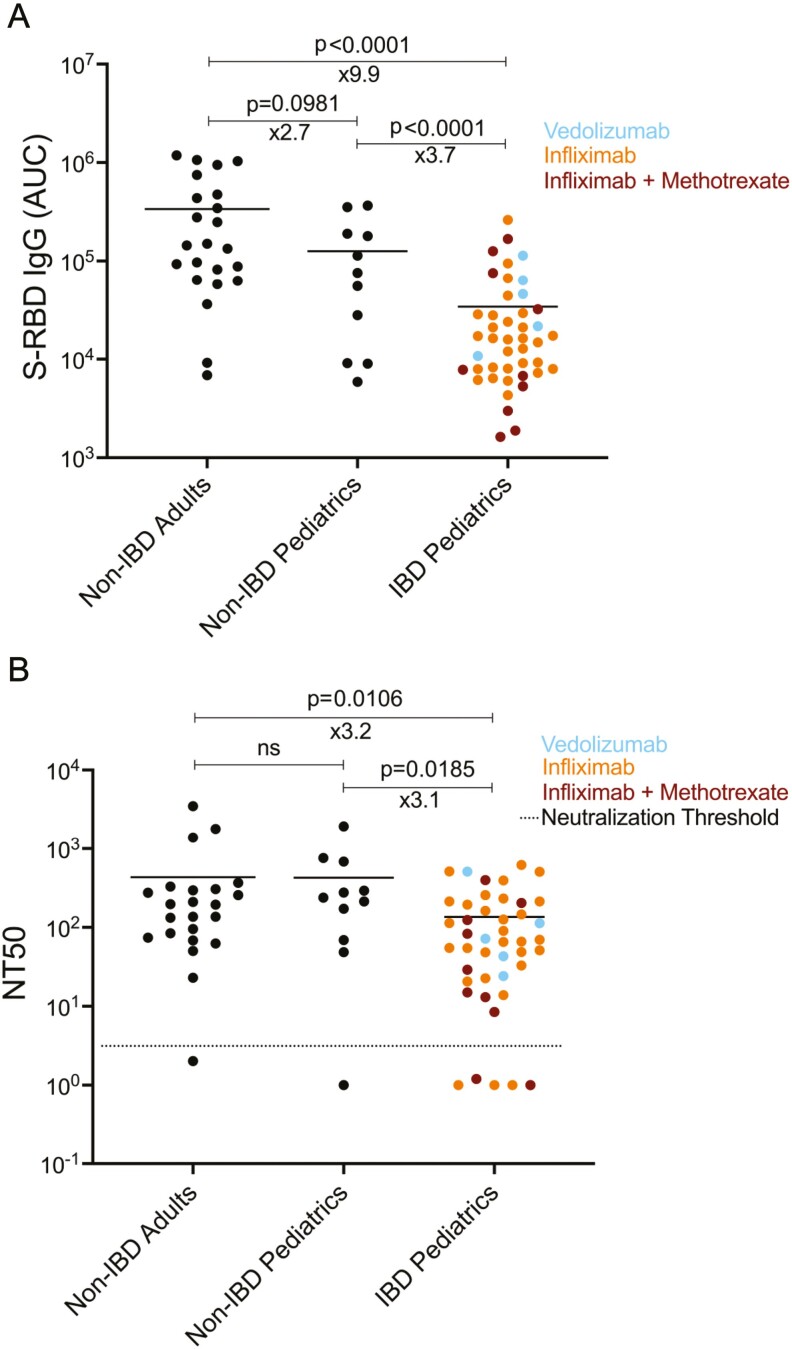
Figure 1.
Comparison of the anti-spike protein IgG antibody levels and neutralization titers of adult non-IBD (inflammatory bowel disease), non-IBD pediatric, and IBD pediatric subjects receiving biologic therapy. A, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain (S-RBD) specific IgG antibody levels measured in serum of non-IBD adult, non-IBD pediatric and IBD pediatric subjects. Area under the curve (AUC) values of serum antibodies were calculated from reciprocal dilution curves in antibody detection assay as described in the “Methods” (n = 23 for non-IBD adults, n = 11 for non-IBD pediatrics, and n = 44 for IBD pediatrics). Blue, orange, and red dots indicate the subjects with vedolizumab monotherapy, infliximab monotherapy, and infliximab + methotrexate cotherapy, respectively. Horizontal bars show the mean value; x values under the significance bars represent the fold changes between the mean values of groups. B, Half-maximal neutralization titer (NT50) values of adult non-IBD, pediatric non-IBD, and pediatric IBD subjects (n = 23 for non-IBD adults, n = 11 for non-IBD pediatrics, and n = 44 for IBD pediatrics). The NT50s of serum samples were measured via a neutralization assay using SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped lentiviruses as described in the “Methods.” Dotted lines indicate the neutralization threshold which was NT50 of 5. Two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test was used to determine the statistical significances.