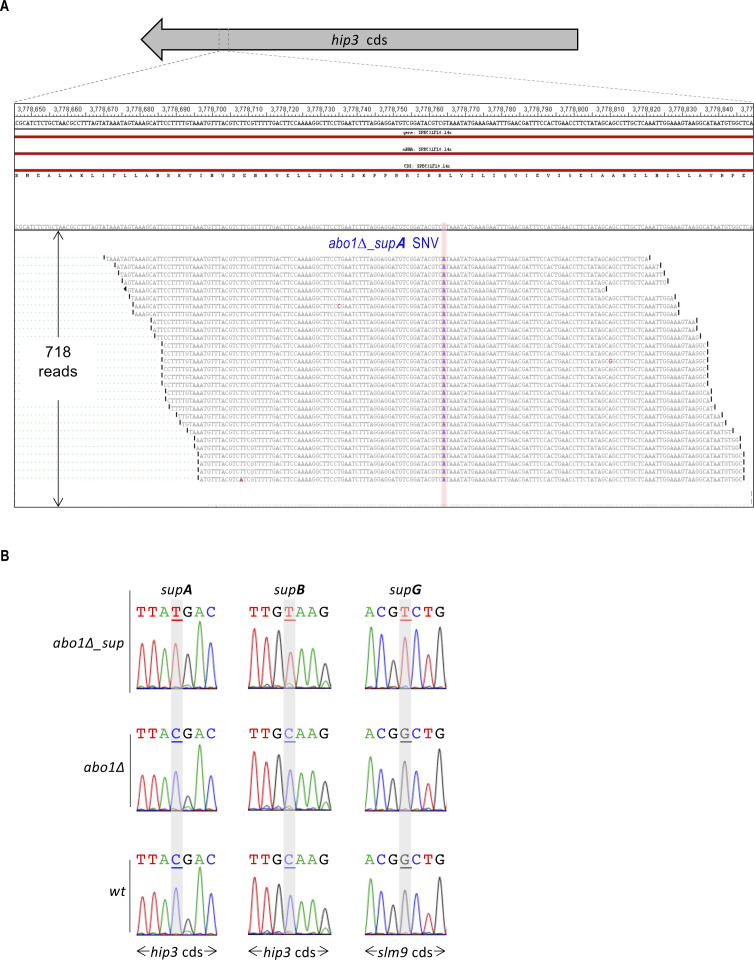
Figure S2. Identification and validation of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) from RNA-seq data.
(A) Example of a SNV identification by the ArrayStar module of the DNASTAR software corresponding to abo1∆_supA RNA-seq data. Alignment of the reads was done over the reference genome of S. pombe (upper sequence) and are shown here for the fraction of hip3 coding sequence that contains the SNV. The SNV G>A is common to all 718 reads and highlighted in blue. This non-sense mutation introduces a stop codon after the amino acid 1,302 of Hip3. Changes of nucleotides that most likely correspond to sequencing errors were also found and are highlighted in red. (B) For three different abo1∆_suppressors (supA, supB and supG), the SNVs found in the RNA-seq data were checked at the genomic level by DNA sequencing, after PCR amplification of the region containing the SNVs. Sequencing traces show, as expected, that SNVs (underlined in gray) are only detected in abo1∆_sup isolates and not in the genomes of wild-type or parental abo1∆ cells. Note that the sequence shown on the electropherograms for hip3 corresponds to the anti-sense strand. Related to Table 1.