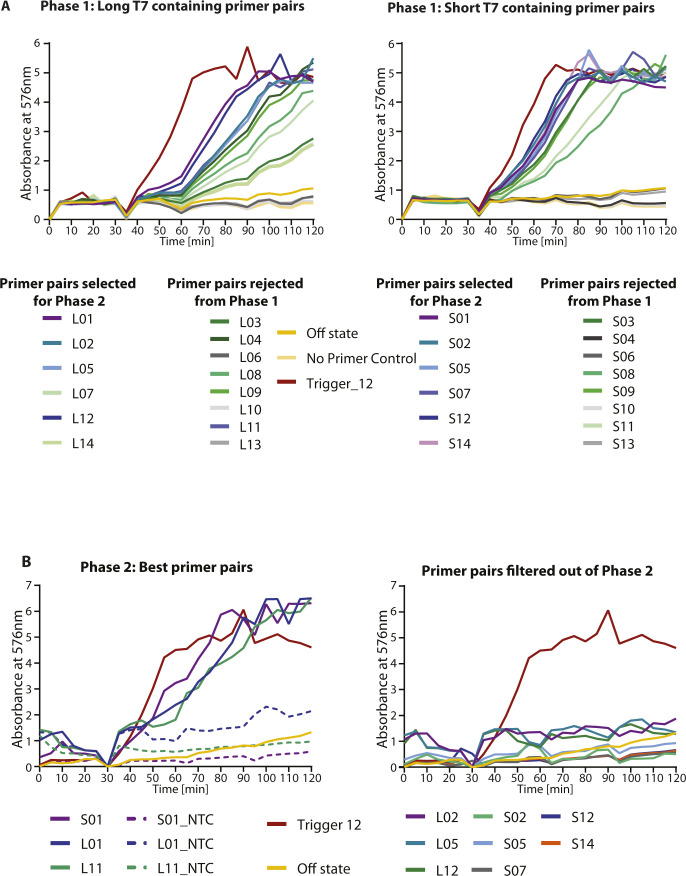
Figure S1. Screen to identify the best NASBA primer pairs.
NASBA coupled with in vitro transcription–translation assay was performed using a fragment of SARS-CoV-2 RNA as template. (A) 28 primer pairs were initially screened and tested for NASBA efficiency (primer sequences in Table S4). Template fragment contains the Trigger for sensor 12. Sensor 12 fused to lacZ was used for the in vitro transcription-translation assay. Data from n = 1 independent experiment show absorbance (576 nm) over time for 108 copies of template RNA. Response to 1013 copies of Trigger RNA (red) was used as a reference. Names of primer pairs are indicated in the index. Two types of forward primers were screened. 14 of the forward primers had a “short” T7 sequence (TAATACGACTCACTATAGG) appended to them, whereas the other 14 forward primers had a longer version of T7 sequence (AATTCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGG) appended. The best primers pairs from here were shortlisted for phase 2 of testing. (B) Phase 2 NASBA primer screen data are shown. Absorbance (576 nm) over time for 104 copies of template RNA is plotted. Response to 1013 copies of Trigger RNA (red) was used as a reference. Shortlisted primer pairs are indicated in the index (details of sequences are in Table S4). Primer pair S01 was selected for further experiments.