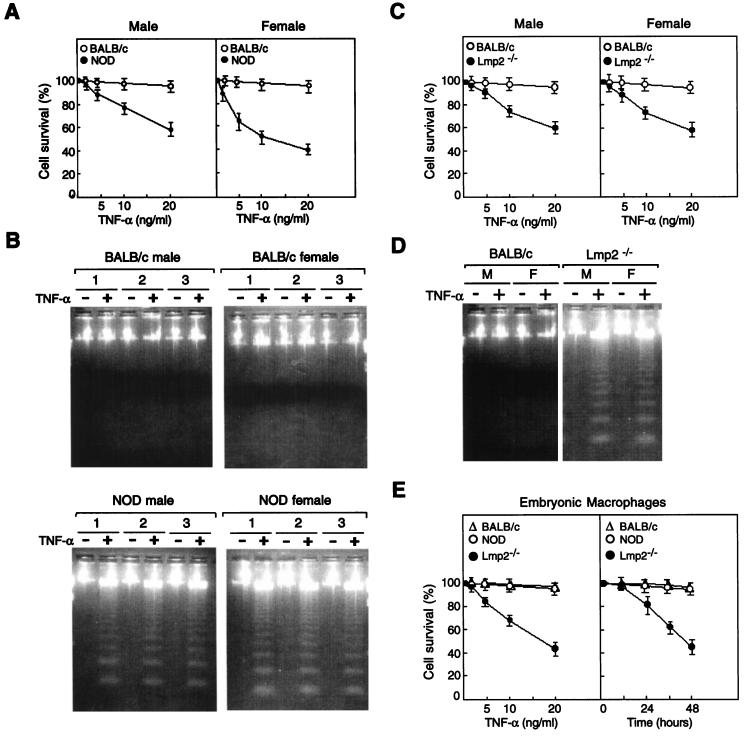
FIG. 5.
Effects of TNF-α on survival of spleen cells derived from BALB/c, NOD, and Lmp2−/− mice. (A) Spleen cells from male or female BALB/c or NOD mice were incubated with various concentrations of TNF-α for 24 h, after which cell viability was assessed by the trypan blue exclusion method. Data are means ± standard deviations (SD) of four replicates from a representative experiment and are expressed as percentages of the survival values for the corresponding non-TNF-α-exposed cells. (B) Spleen cells from three different male or female BALB/c or NOD mice were incubated for 24 h with (+) or without (−) TNF-α (10 ng/ml), after which DNA fragmentation was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. (C) Spleen cells from male or female BALB/c or Lmp2−/− mice were incubated with various concentrations of TNF-α for 24 h, after which cell viability was assessed by the trypan blue exclusion method. Data are means ± SD of four replicates from a representative experiment and are expressed as percentages of the survival values for the corresponding cells not exposed to TNF-α. (D) Spleen cells from three different male (M) or female (F) BALB/c or Lmp2−/− mice were incubated for 24 h with or without TNF-α (10 ng/ml), after which DNA fragmentation was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. (E) Embryonic macrophages obtained from BALB/c, NOD, or Lmp2−/− 13.5-day fetal livers were treated with various concentrations of TNF-α for 24 h or were treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for various time periods, after which cell viability was assessed by the trypan blue exclusion method. Data are means ± SD of four replicates from a representative experiment and are expressed as percentages of the survival values for the corresponding cells not exposed to TNF-α.