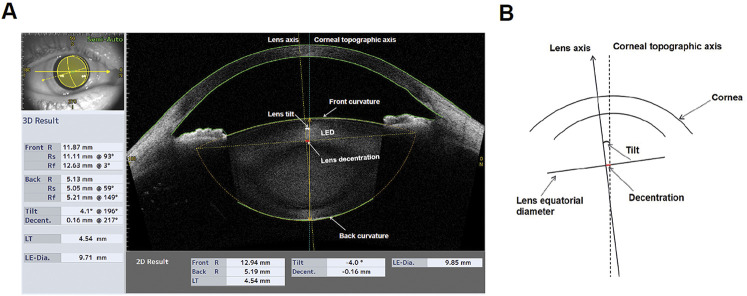
Figure 1.
The measurements of anterior segment and crystalline lens tilt and decentration using CASIA2. A: The representative image showing the 3D result of a crystalline lens. The axis of the crystalline lens (yellow dotted line) and the corneal topographic axis (blue dotted line) were automatically generated by the built-in software. B: The diagram showing the definitions of the tilt and decentration of crystalline lens. The corneal topographic axis is a reference line connecting the fixation point in the topographer to the vertex normal on the cornea. Tilt is the angle of lens axis against the corneal topographic axis, and decentration is the vertical distance from the center of lens equatorial diameter to the corneal topographic axis. Back R = radius of curvature for the lens back surface; Decent. = decentration; Front R = front radius of curvature for the lens front surface; LE-Dia. = lens equatorial diameter; LT = lens thickness; R = radius of curvature; Rs = steep radius of curvature; Rf = flat radius of curvature