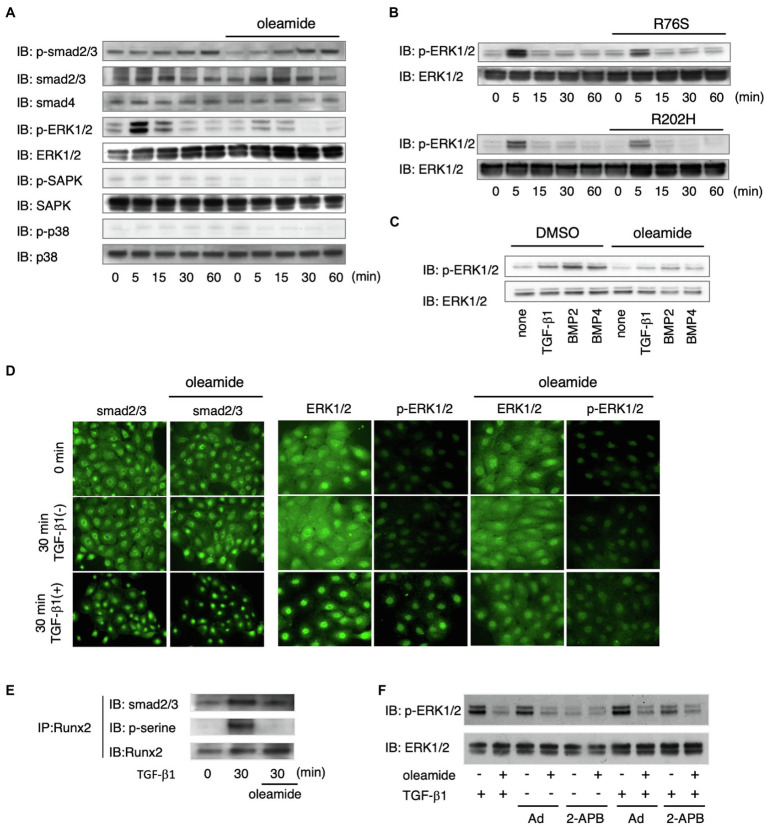
Figure 5.
ERK1/2 phosphorylation is regulated by Cx43-mediated gap junction communication. (A) Phosphorylation of Smad2/3, ERK1/2, and p38 after stimulation by TGF-β1 with or without oleamide. n=5. (B) Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 after stimulation by TGF-β1 after transfection with expression vectors for Cx43 mutants (R76S or R202H). n=5. (C) Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 after stimulation by TGF-β1, BMP2, and BMP4 with or without oleamide. n=5. (D) Localization of Smad2/3 after stimulation by TGF-β1 with or without oleamide. n=5. Localization of ERK1/2 and phospho-ERK1/2 after stimulation by TGF-β1 with or without oleamide. n=5. (E) Immunoprecipitation of Runx2 in TGF-β1-stimulated dental epithelial cells. TGF-β1 induced Runx2 phosphorylation and caused the association of Runx2 with Smad2/3. Phosphorylation of serine residues of Runx2 and binding with Smad2/3 were inhibited by oleamide. n=5. (F) Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in the presence of the IP3R agonist, adenophostin-A (Ad), or the IP3R antagonist, 2-APB, with or without TGF-β1 or oleamide.