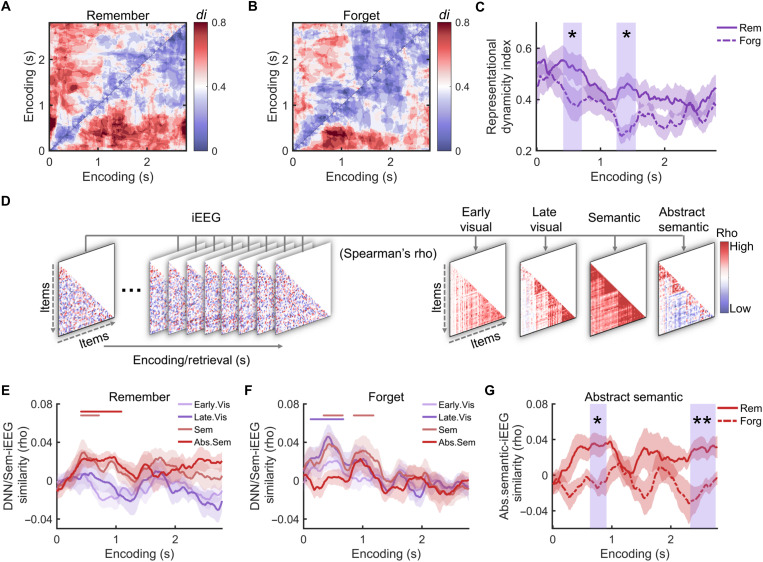
Fig. 2. Representational dynamics and formats during encoding predict long-term memory success.
Representational dynamicity index (di) of subsequently remembered (A) and forgotten items (B). (C) The representational di was significantly greater for remembered than forgotten items within two encoding time windows (blue rectangular shaded time windows). (D) Analysis of representational formats: schematic depiction. During all encoding time windows, neural similarity matrices were created by pairwise correlations of neural representations of items. These neural matrices were correlated with different predictor matrices. The predictor matrices reflected early and late visual representations (derived from a DNN), semantic, and abstract semantic representations (extracted from word embedding analysis), respectively. Representational formats during encoding for subsequently remembered (E) and forgotten items (F). Colored horizontal bars indicate the time windows showing different representational formats. (G) Greater abstract semantic representations of subsequently remembered than forgotten items in two encoding clusters (blue rectangular shaded time windows). *Pcorr < 0.05; **Pcorr < 0.01.