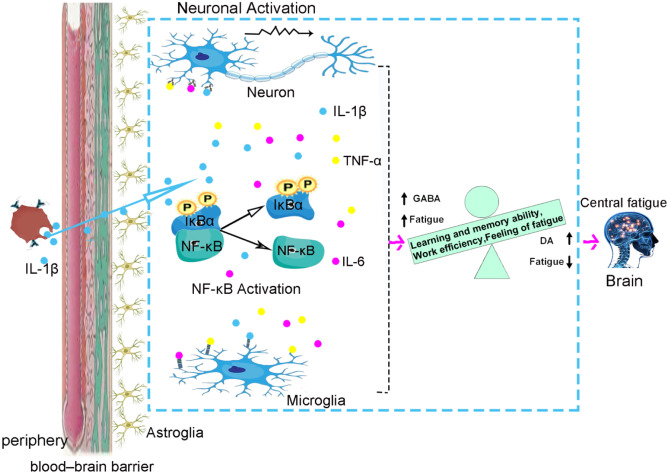
Fig. 2.
NF-κB participates in the development of central fatigue by regulating the balance between excitatory neurotransmitter dopamine (DA) and inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). Under normal circumstances, the metabolism of inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters in the central nervous system is in a state of balance; when this balance is broken, central fatigue can be caused. Both the reward mechanism dominated by excitatory neurotransmitter DA and the inhibitory effect dominated by inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA are related to central fatigue. The balance between the two leading mechanisms is a hot topic in the pathogenesis of fatigue this year. NF-κB can regulate the release of inflammatory cytokines and the effect of inflammatory cytokines on dopamine in ganglion is especially related to fatigue. At the same time, NF-κB has a bidirectional regulatory effect on the neurotransmitter GABA, which affects the occurrence and development of central fatigue