Figure 4. Substrate recognition by Naa30 is similar to NAA50.
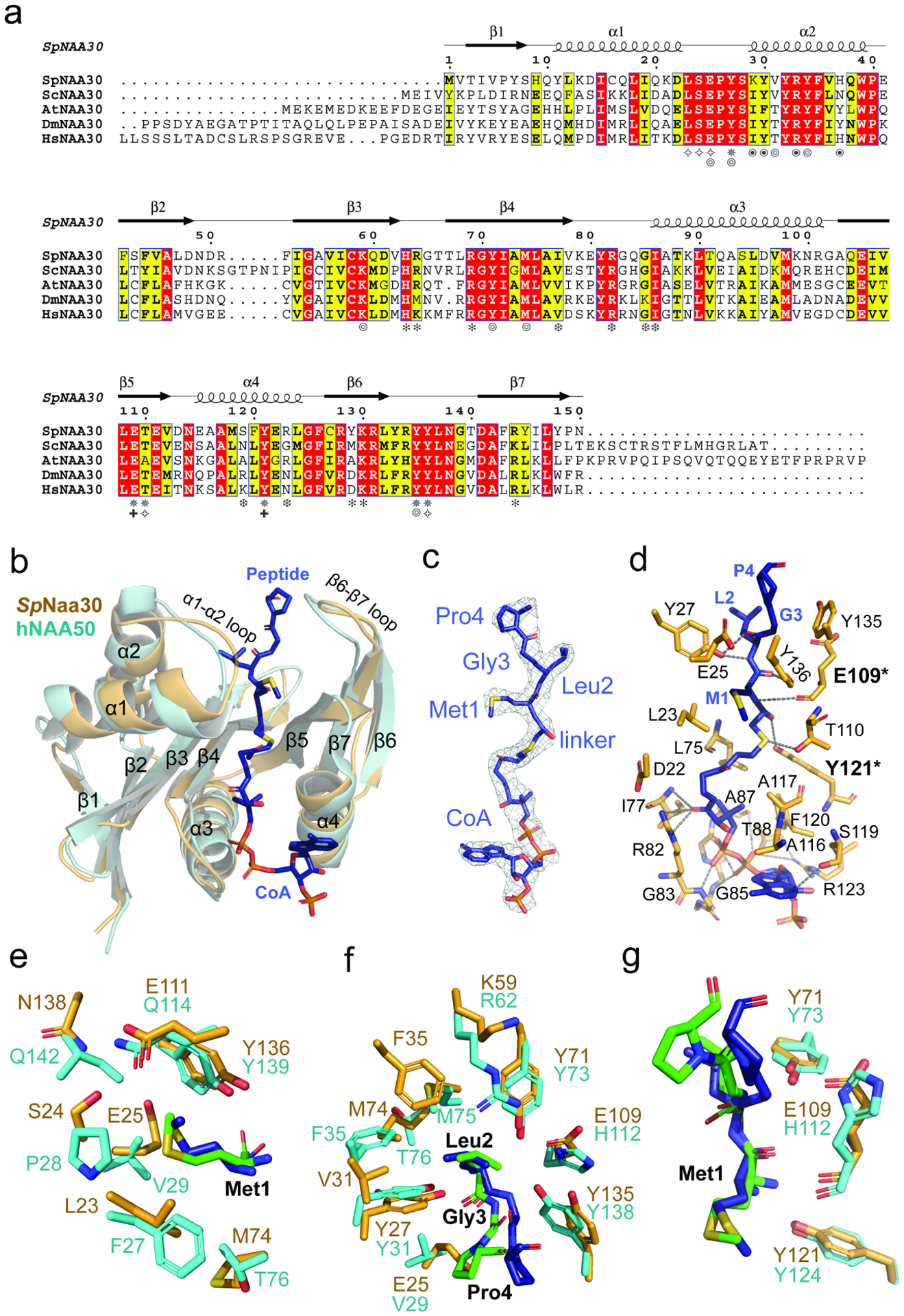
(a) Sequence alignment of Naa30 orthologs from S. pombe (Sp), S. cerevisiae (Sc), A. thaliana (At), D. melanogaster (Dm), and H. sapiens (Hs). Numbering and secondary structure elements for SpNaa30 are indicated above the sequence alignment. Residues of SpNaa30 that contact the peptide backbone (✵), CoA (❆), Met1 (✧), Leu2 (⦾), Naa38 (⦿), IP6 (✽), and catalytic residues (✚) are indicated.
(b) Structural alignment of SpNaa30 (bright orange) with HsNAA50 (cyan), with secondary structure elements indicated.
(C) The fit of the bisubstrate inhibitor in the EM density map. The contour level is 5.0 sigma.
(d) Highlighted polar and hydrophobic interactions between CoA-Ac-MLGP and SpNaa30 are depicted in the 3D view.
(e) Residues forming a hydrophobic pocket surrounding the substrate peptide Met1 sidechain are shown in sticks (Orange, SpNaa30; Cyan, HsNAA50)
(f) Residues forming a hydrophobic pocket surrounding the substrate peptide Leu2 sidechain are shown in sticks. (Orange, SpNaa30; Cyan, HsNAA50)
(g). Residues proposed as catalytic residues are shown in sticks. (Orange, SpNaa30 E109 and Y121; Cyan, HsNAA50 Y73 and H112).
