Fig. 1.
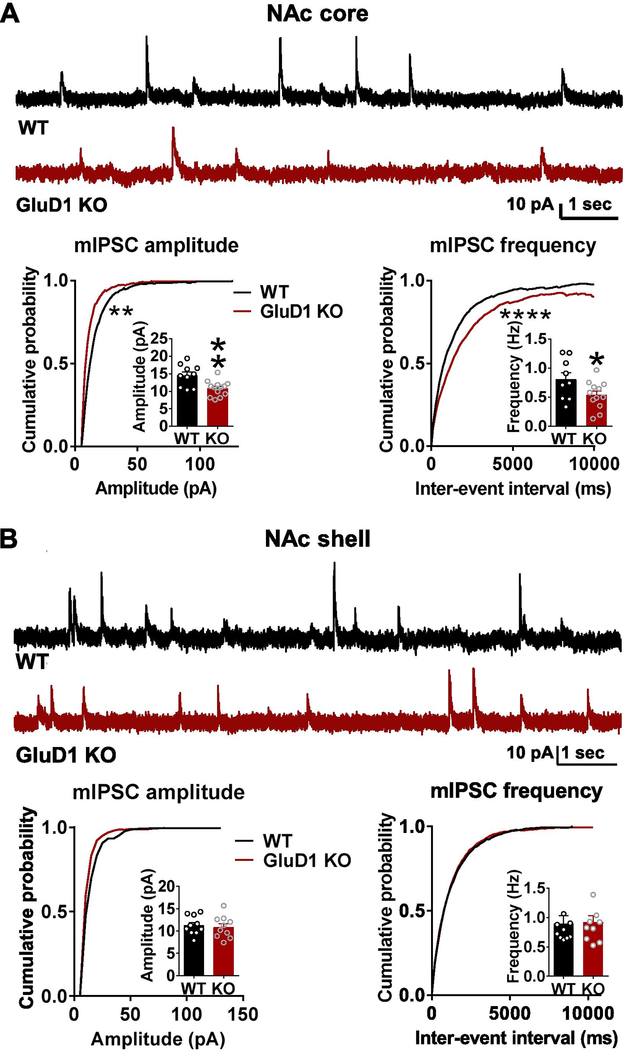
Loss of GluD1 reduces mIPSC amplitude and frequency in the NAc core but not shell. A. A significant reduction in the amplitude of mIPSC was observed in MSNs from NAc core of GluD1 KO (WT: 14.55 ± 0.9841 pA vs. GluD1 KO: 10.82 ± 0.6042 pA, p = 0.0028, Unpaired t-test). Inter-event interval (IEI) was also significantly reduced (p = 0.0096, K-S test) (N = 10–13 from 3 to 4 animals per genotype). A significant reduction in frequency of mIPSC was also observed in GluD1 KO (WT: 0.8073 ± 0.1159 Hz vs. St-GluD1 KO: 0.5390 ± 0.06883 Hz, p = 0.0491, Unpaired t-test). Inter-event interval (IEI) was also significantly reduced (p = 0.0001, K-S test). B. No significant change in mIPSC amplitude or frequency was observed in NAc shell (amplitude: WT: 11.26 ± 0.6671 pA vs. GluD1 KO: 10.87 ± 0.7836 pA, p = 0.7087; frequency: WT: 0.8968 ± 0.1323 Hz vs. GluD1 KO: 0.9187 ± 0.1054 Hz, p = 0.8984; Unpaired t-test) (N = 10 from 3 to 4 animals per genotype). All data are presented as mean ± SEM