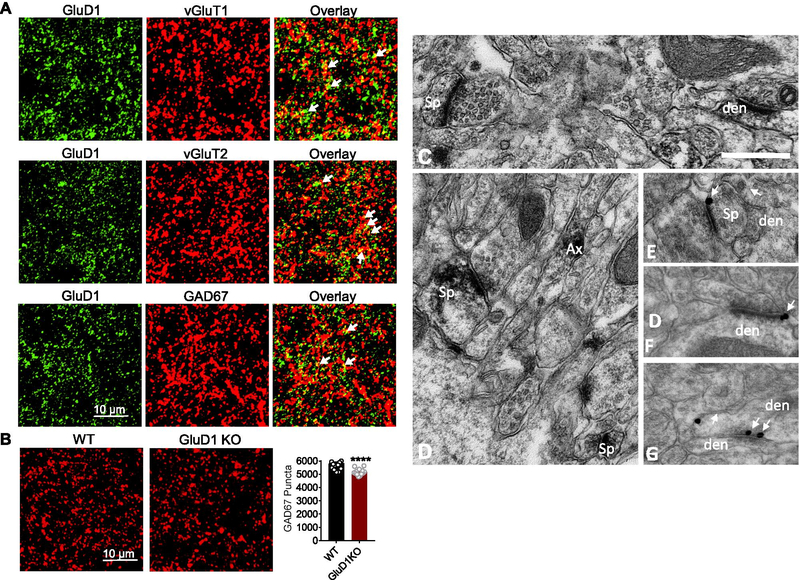
Fig. 3.
GluD1 is localized to both excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the NAc core and loss of GluD1 reduces inhibitory synaptic puncta. A. Representative confocal images from NAc core of GluD1 WT mice showing colocalization of GluD1 with excitatory markers vGluT1 and vGluT2. GluD1 also colocalized with inhibitory marker GAD67. B. Representative coronal images passing through NAc core of WT and GluD1 KO mice immunolabelled for GAD67. Quantification of immunostaining showed significant reduction in GAD67 puncta in GluD1 KO in the NAc core (p < 0.0001; Unpaired t-test). C–G. Electron micrographs of GluD1-immunoreactive profiles in the mouse nucleus accumbens core. (C–D) Examples of GluD1-immunoreactive spine (Sp), dendritic (den) and axonal (Ax) profiles localized with immunoperoxidase, (E–F) GluD1 immunogold labeling (arrows) perisynaptic to asymmetric axo-spinous (E) and axo-dendritic (F) synapses, (G) GluD1 immunogold labeling in the main body of a symmetric axo-dendritic synapse (double arrows). Scale bar: 0.5 μm (valid for A–E)