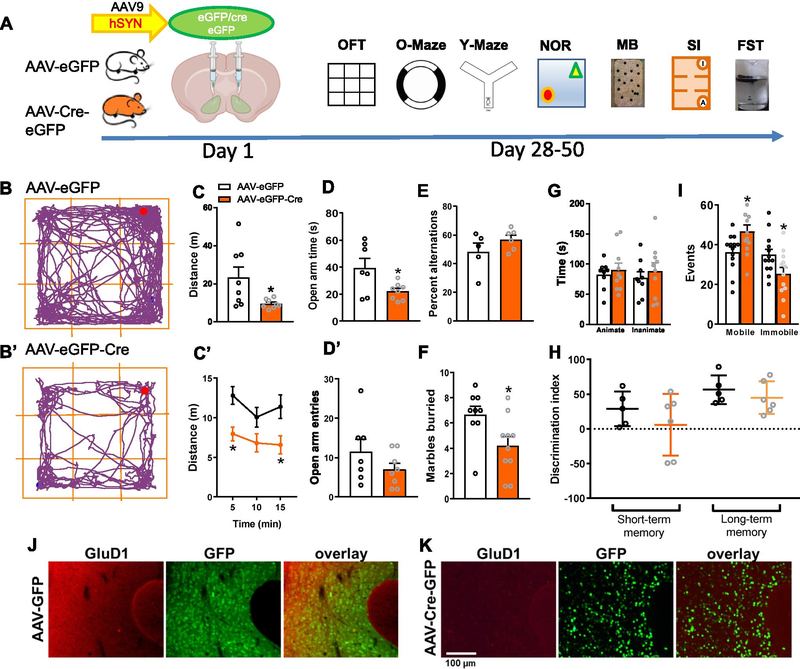
Fig. 5.
Selective ablation of GluD1 from the NAc leads to hypolocomotion and affects anxiety- and depression-like behaviors. A. Experimental timeline, GluD1flox/flox mice received bilateral micro injections of AAV-eGFP and AAV-eGFP-Cre (Day 1) into the ventral striatum (VS), followed by behavioral assays (Day 28–50). B and B’. Representative track plots of the path travelled by mice (VS-AAV-eGFP and VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre). C. VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre group showed significantly less distance traveled compared to the VS-AAV-eGFP group (VS-AAV-eGFP 23.25 ± 5.522 (N = 8) vs VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre 9.532 ± 0.8487 (N = 8), p = 0.0423, unpaired t-test). C’. Locomotor activity per 5 min revealed a significant effect of GluD1 deletion ([F (1, 45)=20.17, p < 0.0001], Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni’s post-hoc test, p < 0.05). D and D’. VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre group showed significantly less time spent in open arm in zero maze (VS-AAV-eGFP 39.29 ± 6.972 (N = 7) vs VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre 21.95 ± 2.204 (N = 8), p = 0.0486) compared to the VS-AAV-eGFP group but no change in number of entries (VS-AAV-eGFP 11.57 ± 3.108 vs. VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre 7 ± 1.558, p = 0.2214, unpaired t-test). E. No change in percent alternations in Y-maze test (N = 5–6, p = 0.2194, unpaired t-test). F. In marble burying test, VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre group buried significantly fewer marbles compared to the VS-AAV-eGFP group (VS-AAV-eGFP 6.667 ± 0.667 (N = 9) vs. VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre 4.2 ± 0.7272 (N = 10), p = 0.0229, unpaired t-test). G. In the sociability test no significant difference in time interacting with the stranger mouse (animate) (N = 9–10, p = 0.5726, unpaired t-test) and inanimate chamber was observed (p = 0.5365, unpaired t-test). H. In novel object recognition test no change in short-term (N = 5–6, p = 0.3133, unpaired t-test) and long-term (p = 0.4098, unpaired t-test) memory was observed. I. In a forced swim test VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre group showed significantly more mobility events (VS-AAV-eGFP 36.23 ± 2.61 (N = 13) vs. VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre 46.58 ± 3.408 (N = 12), p = 0.0251, unpaired t-test) and significantly less immobility events (VS-AAV-eGFP 34.92 ± 2.781 vs. VS-AAV-eGFP-Cre 25.25 ± 3.36, p = 0.0373, unpaired t-test) compared to VS-AAV-eGFP mice. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. J. AAV-eGFP expression and GluD1 expression level was evaluated after the completion of behavioral experiments using immunohistochemical analysis. Sections from brain were evaluated for AAV-eGFP expression (green) and immunohistochemistry was performed for GluD1 (red). K. Downregulation of GluD1 (red) was observed in AAV-eGFP-Cre (green) injected animals