Figure 6. Polyamine Inhibition of eIF5A Controls Translation Termination and HOL1-Fluc Expression.
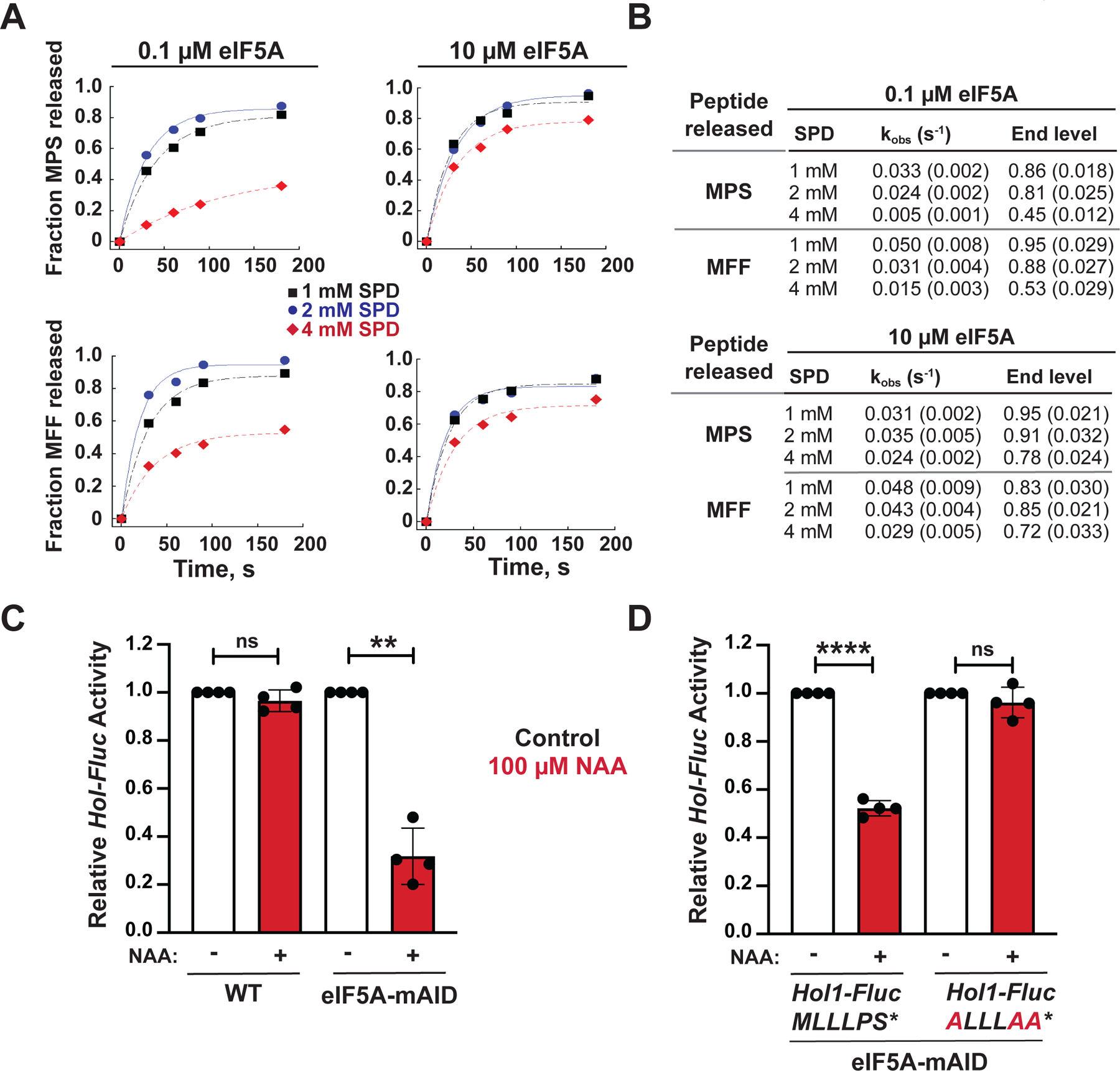
(A) Fractions of MPS* (upper panels) and MFF* (lower panels) peptide release out of total peptide formed in reconstituted translation termination assays performed in the presence of 1 (black squares), 2 (blue circles) or 4 (red diamonds) mM SPD and either 0.1 μM (left panels) or 10 μM (right panels) eIF5A were plotted and fit to a single exponential equation.
(B) Summary of observed rate constants (kobs) and maximum fractions (end levels) of peptide release calculated from the data in (A). Results are representative of three independent experiments; errors in rate constants and end levels are fitting errors from the curves in (A).
(C–D) Relative expression from HOL1-Fluc reporters containing an intact or mutant uORF, as indicated, in a WT strain expressing chromosomal eIF5A (HYP2 ANB1) or an isogenic anb1 hyp2 mutant strain expressing mini auxin-inducible degron-tagged eIF5A-mAID under control of the GAL1 promoter. Luciferase activities were measured from cells grown under control conditions in galactose medium (black) or following the switch to glucose medium and addition of 100 μM NAA to induce depletion of eIF5A-mAID. For each experiment data were normalized to the results obtained under control conditions. Error bars denote SD; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant (Student’s two-tailed t test; n = 3, assayed in duplicate).
