Figure 3.
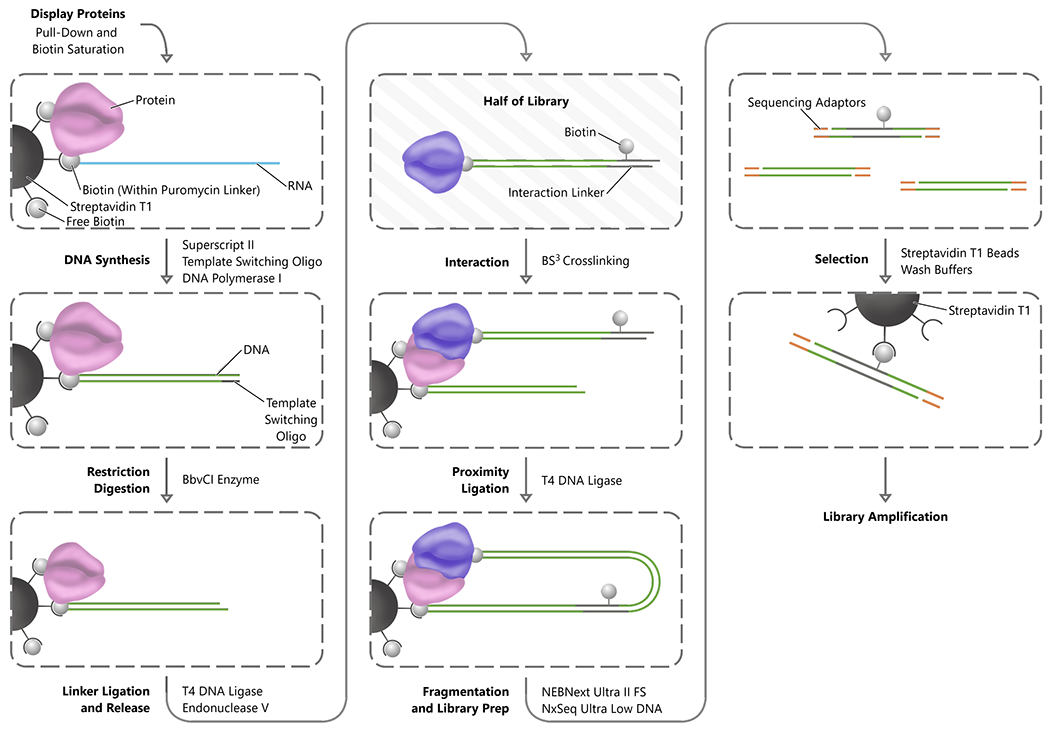
INLISE. Steps are indicated in bold font to the left of each process arrow, and the primary enzymes or reagents used to accomplish each step are indicated to the right of the process arrow. The process begins with the stabilization of the display complexes on streptavidin magnetic beads. Subsequently, the RNA component of each display complex is converted to double-stranded DNA and digested with a non-palindromic restriction enzyme. The library of display proteins is then split into two populations. One half of the display protein complex is ligated to the biotinylated interaction linker and then digested to remove the complexes from the streptavidin beads. The free half of the display protein library is combined with the half still on the beads to perform the interaction step and the interacting proteins crosslinked. The beads are washed to remove nonspecific interactions and then proximity ligation between the display nucleic acids is performed. The DNA is then fragmented and adaptor ligation for sequencing is performed before a final streptavidin selection for the biotin containing interaction linker and library amplification.
