FIGURE 4.
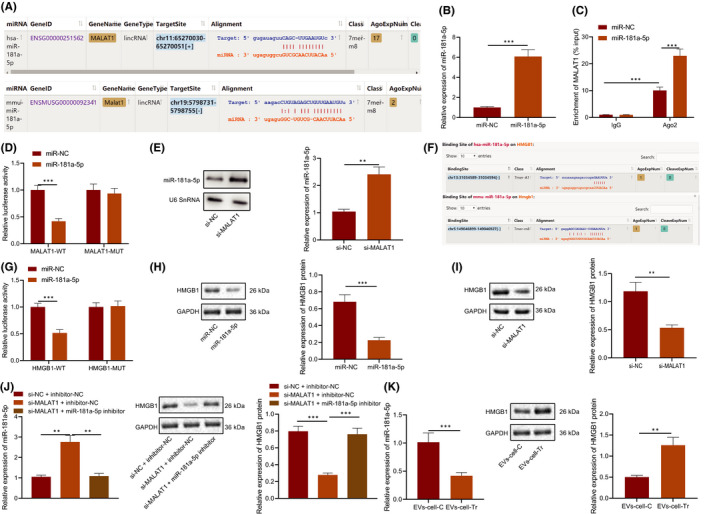
MALAT1 regulated HMGB1 by competitively binding to miR‐181a‐5p. A, Binding sites between MALAT1 and miR‐181a‐5p predicted using bioinformatics analysis. RAW264.7 cells were transduced with miR‐181a‐5p mimic. B, miR‐181a‐5p expression in RAW264.7 cells determined using RT‐qPCR. C, The binding site between MALAT1 and miR‐181a‐5p verified by AGO2 pull‐down assay. D, The targeted binding of MALAT1 to miR‐181a‐5p verified using the dual‐luciferase reporter gene assay. E, The expression of miR‐181A‐5p after MALAT1 silencing detected by RT‐qPCR and Northern blot analysis. F, Binding sites between miR‐181a‐5p and HMGB1 predicted using bioinformatic analysis. G, The targeted binding of miR‐181a‐5p to HMGB1 verified using the dual‐luciferase reporter gene assay. RAW264.7 cells were transduced with miR‐181a‐5 mimic. H, HMGB1 protein level in RAW264.7 cells measured using Western blot analysis. RAW264.7 cells were transduced with si‐MALAT1. I, HMGB1 protein level in RAW264.7 cells measured using Western blot analysis. RAW264.7 cells were transduced with miR‐181a‐5 inhibitor and si‐MALAT1. J, HMGB1 protein level in RAW264.7 cells measured using Western blot analysis. RAW264.7 cells were treated with EVs from caerulein‐treated MPC‐83 cells. K, miR‐181a‐5p expression and HMGB1 protein level in RAW264.7 cells measured using RT‐qPCR and Western blot analysis, respectively. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. Data are shown as the mean ± standard errors
