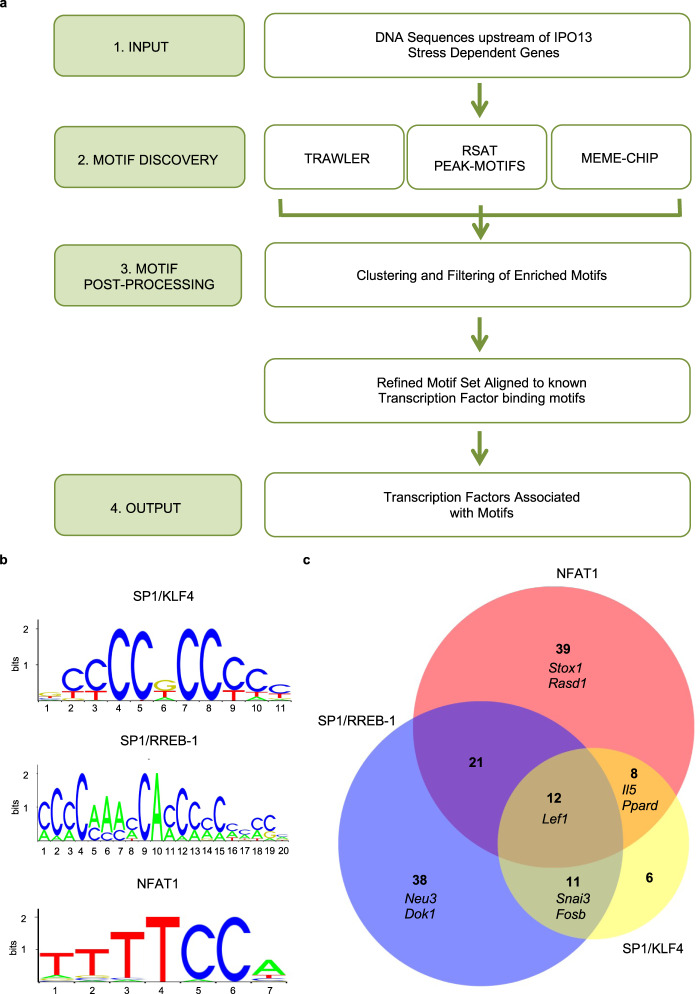
Fig. 3. TF binding motif enrichment in the IPO13-dependent stress transcriptome contributing to the IPO13 dependent oxidative stress transcriptome.
a Pipeline for motif discovery. Genome coordinates identified were derived from UCSC Mouse Encode from ChIP Seq experiments performed in mESCs for the H3K4me1, H3K4me3, and H3K27ac histone marks. Genomic regions enriched for these marks were associated with a gene using GREAT software from Stanford Bioinformatics, and then filtered to include only the 277 IPO13-dependent stress-regulated genes identified (see text). Overlapping genomic regions were merged using Galaxy before collecting the FASTA sequences for the final (1) set of genomic regions using UCSC Mouse Encode. FASTA sequences were input (2) into each of the Motif Discovery Tools Trawler, RSAT Peak-Motif, and MEME-CHIP to identify overrepresented motifs. Motifs identified by each tool were consolidated (3) and then inputted into STAMP to cluster and merge motifs, removing redundant or nonsense motifs. The final set of refined motifs were aligned to known TF binding motifs using the JASPAR library via STAMP. The output set (4) of TFs for each motif set was ranked by STAMP according to the similarity of the input motif to matched TF motif. b Candidate motifs are overrepresented in the IPO13 dependent stress transcriptome identified in (a) with consensus TFs binding them indicated. c Venn diagram of the genes containing one or multiple motifs from (b) in the IPO13 dependent stress transcriptome, with numbers of genes indicated in the different unique/overlapping parts of the diagram, together with the names of the genes selected for RT-qPCR validation i.e. Stox1 and Rasd1 contain the motif aligned to the NFAT1 binding motif, Neu3, and Dok1 contain the motif aligned to the SP1 and RREB-1 binding motif, Il5, and Ppard contains the motif aligned to the NFAT1 binding motif and to the SP1 and RREB-1 binding motif, Snai3, and Fosb contain the motif aligned to the SP1 and RREB-1 binding motif and to the SP1 and KLF4 binding motif and Lef1 contains the motif aligned to all three of the TF binding motifs. RT-qPCR validation for selected genes is shown in Sup. Figure 3.