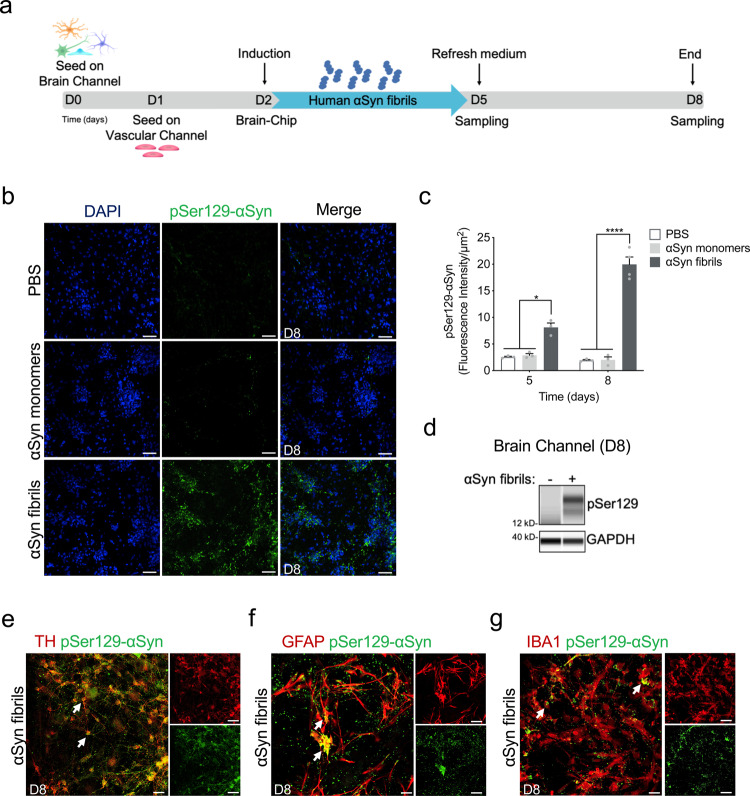
Fig. 3. Pathological αSyn accumulation in the brain channel following exposure to human αSyn fibrils.
a Experimental design for assessing the effects of αSyn toxic aggregates (fibrils) in the Substantia Nigra Brain-Chip, including the seeding in the Brain-Chip, the timeline for medium changes, as well as sampling times. b Immunofluorescence micrographs show the accumulation of phosphorylated αSyn (green, phospho-αSyn129 staining; blue, DAPI) at day 6 post-exposure (D8). Pathology is absent in the brain channel following exposure to monomer or PBS. Scale bars: 100 μm. c Quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity in each group at day 3 and 6 post-exposure (D5 and D8, respectively). Statistical analysis is two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (n = 3–4 independent chips with 3~5 randomly selected different areas per chip, *P = 0.0103, ****P < 0.0001 compared to monomeric group). Error bars represent mean ± SEM. d Western blotting analysis of cell lysates from the brain channel shows significant intracellular phosphorylation of αSyn at Ser129 (MW: 18 kDa) following exposure to αSyn fibrils, whereas there was no effect upon exposure to the PBS. For loading control, equal amounts of protein were immunoblotted with GAPDH antibody (MW: 37 kDa). e Confocal images of double immunostaining for phospho-αSyn129 (green) and tyrosine hydroxylase (red, TH), in the brain channel at day 6 post-exposure (D8) to αSyn fibrils (white arrow). Scale bars: 50 μm. f, g αSyn fibrils are taken up by astrocytes and microglia (white arrow), as evidenced by double immunostaining for phospho-αSyn129 (green) and either glial fibrillary acidic protein (red, GFAP) for astrocytes or ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (red, IBA1) for microglia in the brain channel at day 6 post-exposure (D8) to αSyn fibrils. Scale bars: 50 μm.