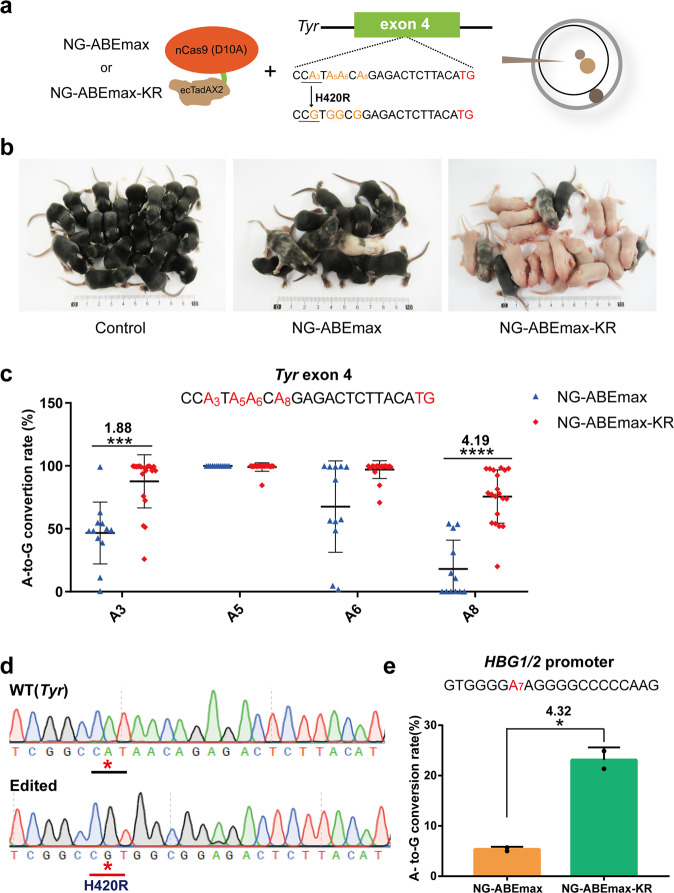
Fig. 4. Application of NG-ABEmax-KR for the generation of mice disease models and human gene therapy.
a Schematic of editing activity comparison of NG-ABEmax and NG-ABEmax-KR in mouse embryos via zygote intracytoplasmic injection. b The newborn pups (days 10) produced by intracytoplasmic injection of NG-ABEmax or NG-ABEmax-KR mRNA and Tyr sgRNA. The Tyr mutant mice (H420R) are in white and the wild-type are in black, respectively. Control represents only ddH2O injection. c Statistical analysis of on-target A-to-G base conversions induced by NG-ABEmax (n = 12), NG-ABEmaxKR (n = 20) in all pups. Data are mean ± s.d for the indicated numbers of mice. Each A base was highlighted in red. ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 by Student’s unpaired two-sided t test. Exact P value of A3 = 0.00023, exact P value of A8 = 0.00001. d Sanger sequencing chromatograms confirmed the editing events. The desired mutation was highlighted with red star. e Boosted editing efficiency (A7) of NG-ABEmax-KR at HBG1/2. Error bars indicate mean ± s.d. (n = 2 independent experiments). *P < 0.001 by Student’s unpaired two-sided t test. Exact P value = 0.010120. Source data are available in the Source data file.