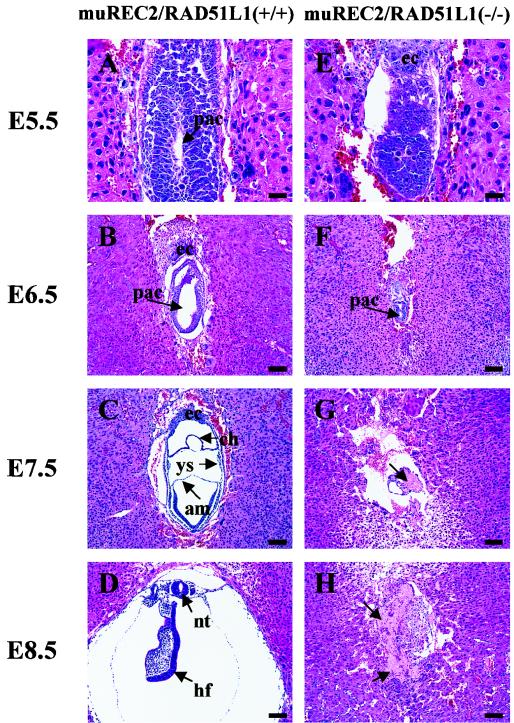
FIG. 3.
Histological sections of wild-type and muREC2/RAD51L1−/− embryos grown in utero. Sagittal sections are shown. All sections were stained with H&E. (A to D) Wild-type embryos; (E to H) muREC2/RAD51L1−/− embryos. (A) E5.5 wild-type embryo (early egg cylinder stage). Note the appearance of the proamniotic cavity and the clearly differentiated embryonic and extraembryonic ectoderm. (B) E6.5 wild-type embryo (egg cylinder stage). Note the formation of an exocoelomic cavity and enlargement of the proamniotic cavity (pac). (C) E7.5 wild-type embryo. The three germ layers are apparent. The yolk sac (ys), chorion (ch), and amnion (am) are clearly seen. (D) E8.5 wild-type embryo. More structures are formed (neural tube [nt], head fold [hf], etc.). (E) E5.5 mutant embryo. The embryonic region is reduced. No proamniotic cavity is seen. (F) E6.5 mutant embryo. There is evidence of a great loss of embryonic tissue and narrowing of the proamniotic cavity. (G) E7.5 mutant embryo. Only traces of embryonic tissue are left. Resorption is evident (indicated by the arrow). (H) E8.5 mutant embryo. The embryo is completely resorbed. The arrows indicate the pac. ec, ectoplacental cone. Bars, 100 μm.