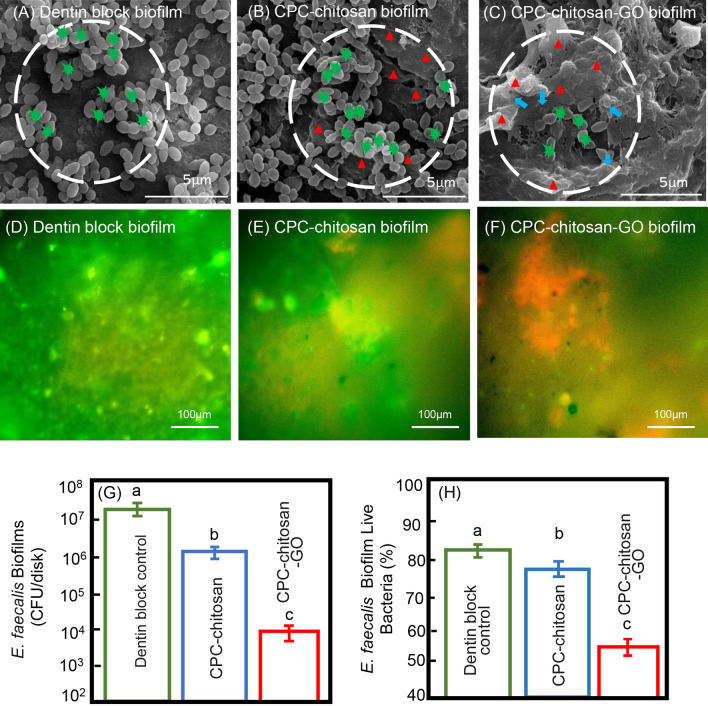
Fig. 4.
A clinical isolate of E. faecalis were used for comparison. Surface characteristics of CPC-chitosan-GO scaffold and antibacterial effects of CPC-chitosan-GO disks on E. faecalis clinical isolate: A The dentin control group. B There were E. faecalis colonies spreading among the interlaced CPC-chitosan, and C there were few E. faecalis cells spreading on CPC-chitosan-GO. The green stars show E. faecalis colonies, the red triangles show the CPC-chitosan composites and the blue arrows indicate GO powder. Live and dead assay of bacterial biofilms on CPC-chitosan scaffold and CPC-chitosan-GO disks at 24 h (D–F). Clinical isolate E. faecalis biofilms were served as control (D), CPC-chitosan group (E) were covered by live bacteria, and the CPC-chitosan-GO group (F) had more dead bacteria with red staining. G CPC-chitosan-GO group demonstrated much lower biofilm CFU, compared to CPC-chitosan group (p < 0.05). H The percentage of live E. faecalis on CPC-chitosan scaffold and CPC-chitosan-GO disks. Dissimilar letters indicate significantly different values (p < 0.05)