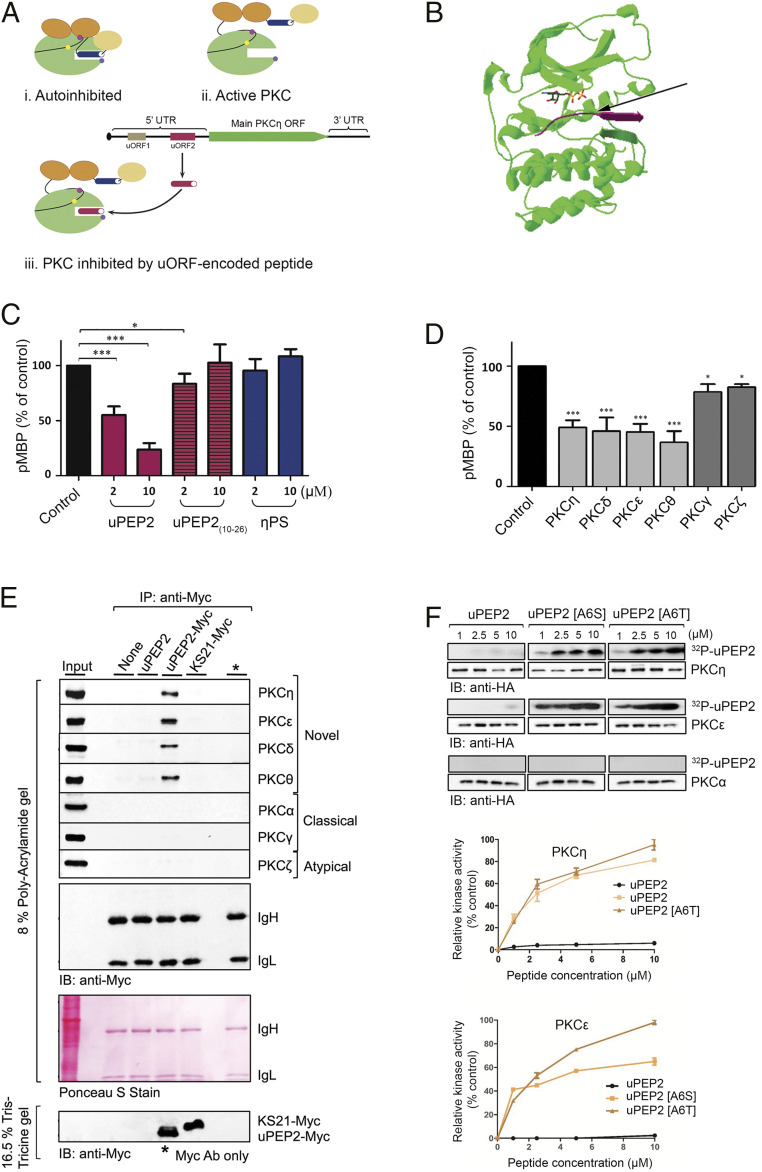
Fig. 2.
uORF2-encoded peptide inhibits the kinase activity of novel PKCs. (A) The active/inactive states of PKCs: (i) In the autoinhibited state, the PS domain (dark blue cylinder) binds to the kinase domain (green circle) leading to its inhibition. (ii) In the active state, the PS domain is detached from the kinase domain due to a conformation change. (iii) In the proposed state, the kinase domain is bound by the uORF2-encoded peptide (dark red cylinder) and thus inhibited. Oval shapes represent other PKC domains, and small circles represent phosphorylation sites. (B) A general view of the proposed PKC-η–uPEP2 complex. The model shows the catalytic domain of PKC-η (green) bound to ADP (stick model) and to residues 1 to 9 of uPEP2 (magenta). The nonphosphorable alanine 6 residue of uPEP2 (marked by an arrow) is positioned in the phosphorylation site by a small β-sheet formed by residues 7 to 9 of uPEP2 and residues 514 to 516 of PKC (magenta and green ribbons, respectively), which are unstructured in the unbound state. The model suggests several hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions (SI Appendix, Fig. S2) that may explain the stability and specificity of the complex. (C) uPEP2 inhibits the kinase activity of PKC-η. Kinase assays were performed using MBP as a substrate with/without tested peptides. uPEP2 was a more effective inhibitor than a peptide containing the internal PS motif of PKC-η (η-PS) and a peptide derived from uPEP2 but lacking its N-terminal part (uPEP2(10–26)). (D) uPEP2 inhibits the kinase activity of novel PKCs. Kinase activity assays depicting novel PKCs (light gray) and other PKC members (dark gray) were performed as in C. The data shown are means of three independent experiments. Details of kinase assays in C and D are presented in SI Appendix, Fig. S3. (E) uPEP2 selectively binds to novel PKC isoforms. HEK-293T lysates overexpressing different PKC isoforms were subjected to immunoprecipitation using protein A/G beads preadsorbed with anti-Myc antibody and Myc-tagged peptides (uPEP2, uPEP2-Myc, or the nonrelevant control peptide KS21-Myc). (F) Altering alanine at position 6 into S/T converts uPEP2 into an excellent substrate of novel PKC-η and PKC-ε but not PKC-α. Kinase assays were performed as in C using γ-ATP and uPEP2, uPEP2[A6S], or uPEP2[A6T] as substrates. P values calculated using one-way ANOVA. ***P ≤ 0.001 and *P ≤ 0.05.