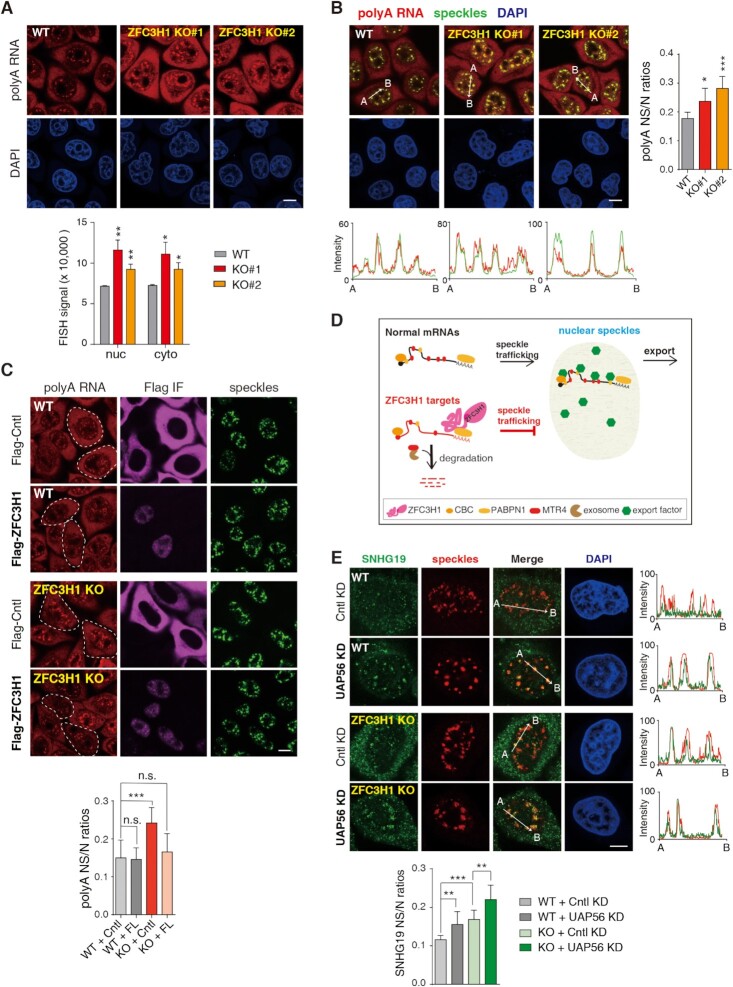
Figure 1.
ZFC3H1 depletion results in polyA RNA accumulation in NSs. (A) (Top) FISH with an oligo(dT) probe to detect polyA RNAs in WT and ZFC3H1 KO cells. Scale bar, 10 μm. (Bottom) Quantification of nuclear and cytoplasmic FISH signals of polyA RNAs in WT and ZFC3H1 KO cells. FISH signals of 30 cells were calculated in each experiment. Error bars, standard deviations (n = 3). (B) (Left) Confocal microscopic imaging to examine the colocalization of polyA RNAs with NSs in WT and ZFC3H1 KO cells. FISH with an oligo(dT) probe and IF using the SC35 (as an NS marker) antibody were carried out. The red and green lines in the graphs show the intensities of FISH and SC35 IF signals along the freely positioned arrow indicated from A to B, respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm. (Right) Quantification of NS/N ratios of polyA RNA signals in WT and ZFC3H1 KO cells. Error bars, standard deviations (n = 15). (C) (Top) Confocal microscopy analysis to examine the effect of Flag-DDX3 (Cntl) and Flag-ZFC3H1 on polyA RNA signals in WT and ZFC3H1 KO cells. FISH with an oligo(dT) probe and IF using Flag and SON (as an NS marker) antibodies were carried out. Exemplified cells with proper expression of Flag-ZFC3H1 or Flag-Cntl are indicated by white dashed lines. Scale bar, 10 μm. (Bottom) Quantification of polyA RNA NS/N ratios in cells transfected with corresponding constructs. Error bars, standard deviations (n = 10). (D) The illustration of possible fate of normal mRNAs and ZFC3H1 targets. Normal mRNAs traffic into NSs to gain export competence and are consequently exported to the cytoplasm. ZFC3H1 prevents its target RNAs trafficking into NSs and facilitates their degradation. (E) (Top) Confocal microscopic imaging to examine the colocalization of endogenous SNHG19 RNA with NSs in WT and ZFC3H1 KO cells treated with Cntl or UAP56/URH49 siRNAs. FISH with an SNHG19-specific probe and IF using a SON (as an NS marker) antibody were carried out. The green and red lines in the graphs show the intensities of FISH and SON IF signals along the freely positioned arrow indicated from A to B, respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm. (Bottom) Quantification of NS/N ratios of SNHG19 RNA. Error bars, standard deviations (n = 10). Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s., not significant.