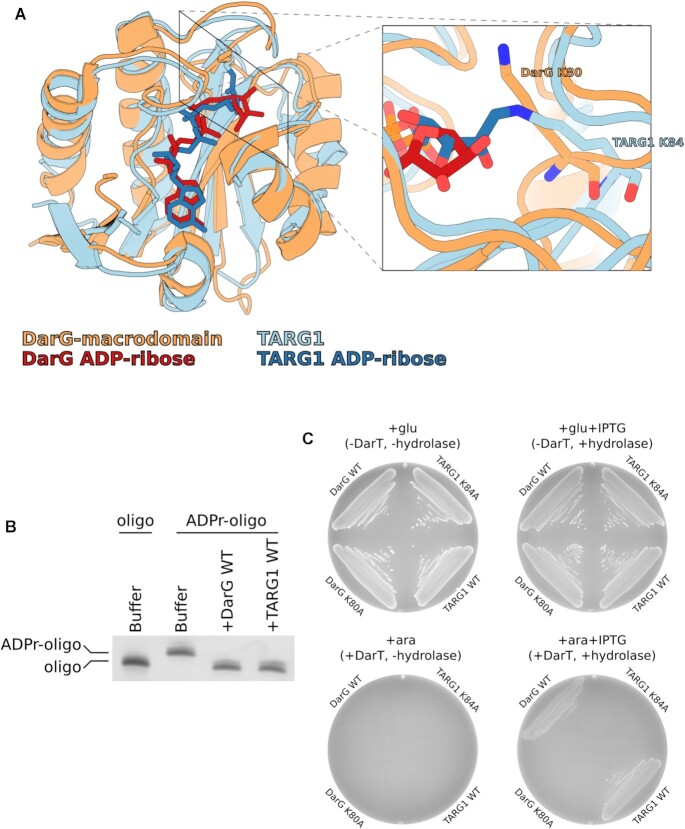
Figure 1.
TARG1 removes thymidine-linked ADP-ribose from DNA and confers resistance to DarT toxicity in bacteria. (A) Structural comparison between TaqDarG-macrodomain (orange) bound to ADP-ribose (red) and TARG1 (light blue) with a covalent lysyl-ADP-ribose linkage (dark blue). To the right is a detailed view of the DarG catalytic lysine 80 (orange sticks) and TARG1 catalytic lysine 84 (blue sticks). (B) UV detection of DarT ADP-ribosylated DNA oligonucleotide de-ADP-ribosylation reactions with TaqDarG-macrodomain and TARG1. (C) Bacterial DarT toxicity rescue assay in BL21 DE3 using pBAD DarT and pET encoding DarG-macrodomain WT, DarG-macrodomain K80A, TARG1 WT or TARG1 K84A. pBAD expression is controlled with glucose or arabinose and pET expression is controlled with IPTG.