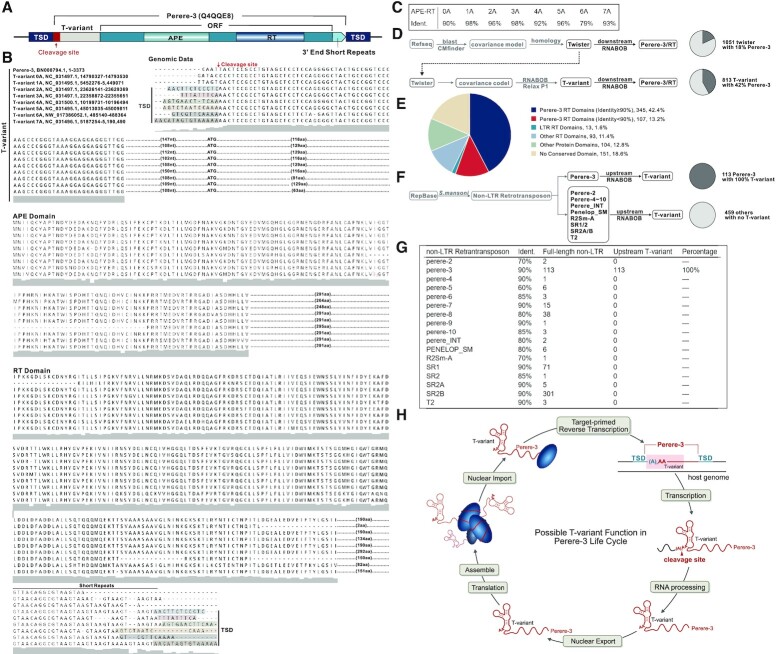
Figure 2.
Genomic location of T-variant and Perere-3. (A) Schematic representation of the Perere-3 non-LTR retrotransposable element (UniProtKB Code: Q4QQE8) containing T-variant. T-variant sequences at the retrotransposon 5′ ends are marked as light grey boxes, with the different numbers of As at the cleavage site highlighted in the red box. The single open reading frame (ORF) of perere-3 is indicated as a turquoise box, with the embedded gradient boxes denoting the APE (pea green) and RT domains (sky blue). The light green arrow after the ORF represents the short repeats at the 3′ end. The TSDs flanking the whole retrotransposon element are marked as navy-blue boxes. (B) Alignment of representative (0–7A) T-variant sequences with accession numbers and genomic locations. The site of ribozyme self-cleavage is marked with the red arrow. TSDs are shown in shaded boxes at the 5′ and 3′ ends and the short 3′ sequence repeats indicated. The predicted amino acid sequences of the APE and RT domains downstream of the T-variants in Perere-3 retrotransposable elements are aligned. Similarities between the two domains are indicated as a grey shadow below the sequences. (C) Identity of T-variant downstream endonuclease-reverse transcriptases compared to the reported perere-3 non-LTR retrotransposon (56). (D) Pipeline for identification of twister (upper path) and T-variant sequences (lower branch-point). T-variants were identified by retaining the conserved structural components of Twister and relaxing the constraints on the P1 stem as an additional search criterion. The pie charts indicate the percentage of the published twister (top) and the enrichment of T-variant (bottom) sequences in S. mansoni that possess RT domains within 10kb downstream of the ribozyme sequence (marked as charcoal grey). (E) Analysis of the 813 T-variant downstream sequences in S. mansoni by domain identity: Perere-3 RT domains ≥ 90% (Blue segments), Perere-3 RT domains 60–90% (Red segments), LTR RT domains (green), other RT domains (light blue), other protein domains (light green) and no conserved domain (sand). Chromosomal locations and accession numbers are listed in Supplementary Table S2. (F) Pipeline for the reciprocal searching of all 17 non-LTR retrotransposons classes in S.mansoni. The full-length published non-LTR retrotransposon sequences were obtained from Repbase (https://www.girinst.org/repbase) and searched against the S.mansoni genome. The upstream sequences (1 kb) of these non-LTR retrotransposons were searched for T-variants with RNABOB. The pie charts indicate the percentage of the full-length Perere-3 (100%) and other non-LTR retrotransposons in S. mansoni that possess T-variants up to 1kb upstream (marked as charcoal gray). (G) Counts of each full-length non-LTR retrotransposons with respective identities and their upstream T-variants. (H) The Possible function of T-variants in the Perere-3 non-LTR retrotransposon replication cycle.