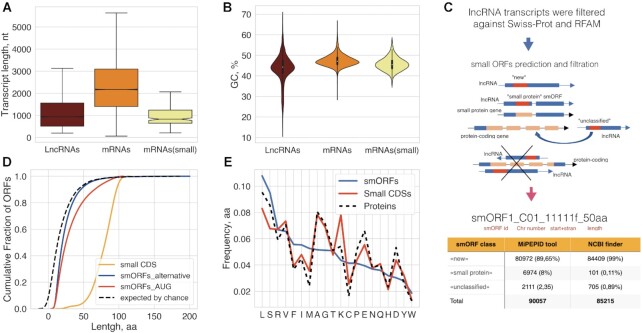
Figure 1.
Prediction and classification of small ORFs. (A) Boxplot showing the length comparison of lncRNAs, mRNAs and small RNAs (code for functional proteins below 100aa). The median, quartiles, and 5th and 95th percentiles are shown. (B) Comparison of GC contents of lncRNAs, mRNAs and small RNAs. (C) Pipeline of smORFs prediction and classification. (D) Cumulative distribution of different CDS lengths; ‘random smORFs’ refer to smORFs expected to occur by chance; the median lengths are 25aa and 20aa for MiPEPID-smORF and NCBI ORF finder, respectively; ∼26% MiPEPID-smORFs had the length more than 40 aa. (E) Comparison of amino acid compositions of functionally characterized proteins (including small CDSs, <100aa) and AUG-started smORF-encoded peptides. smORFs were enriched in leucine (chi-square P-value < 10–15), isoleucine (chi-square P-value < 10–15), phenylalanine (chi-square P-value < 10–15) in comparison to functional proteins.