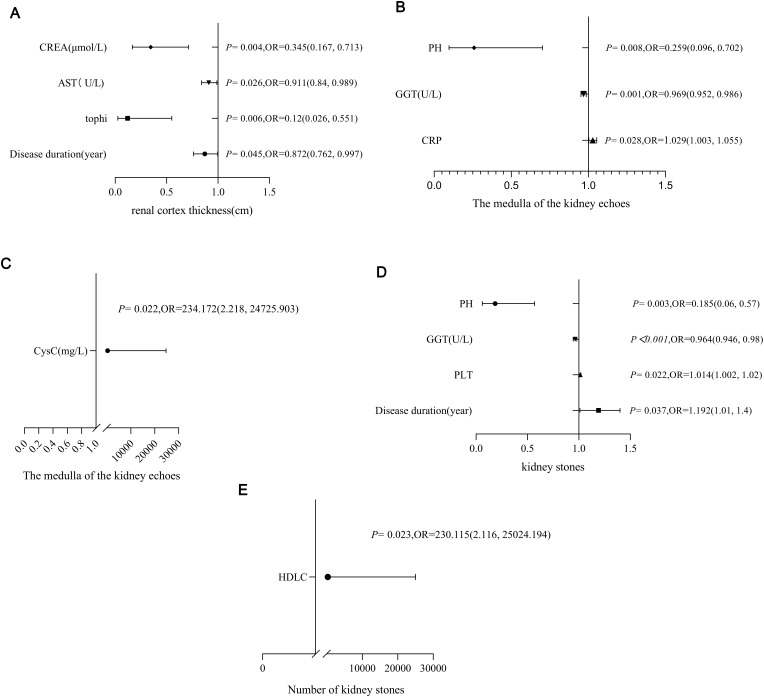
Figure 3.
Logistic regression analysis of renal ultrasound parameters and laboratory indexes in patients with gout. P < 0.05: statistically significant. (A) Risk factors for renal cortical thickness, showing that disease duration, AST, CREA and tophi were risk factors of renal cortical thinning in patients with gout. [OR (95% CI) were respectively 0.872 (0.762, 0.997), 0.911 (0.84, 0.989), 0.345 (0.167, 0.713), 0.12 (0.026, 0.551)]. (B and C) Risk factors for renal medulla echo, showing that CRP and CysC are risk factors of renal hyperechogenicity of renal medulla in patients with gout [OR (95% CI) were respectively 1.029 (1.003, 1.055), 234.172 (2.218, 24725.903)].PH and GGT are protective factors of renal hyperechogenicity of renal medulla in patients with gout [OR (95% CI) were respectively 0.259 (0.096, 0.702), 0.969 (0.952, 0.986)], Among them, GGT protection factor is weak. (D and E) Risk factors for the presence of renal stones, showing that disease duration, PLT and HDL-C are the risk factors for gout patients with nephrolithiasis [OR (95% CI) were respectively 1.192 (1.01, 1.406), 1.014 (1.002, 1.027), 230.115 (2.116, 25024.194)], PH and GGT are protective factors of kidney stone formation in patients with gout [OR (95% CI) were respectively 0.185 (0.06, 0.574), 0.964 (0.946, 0.983)], Among them, GGT protection factor is weak.
Abbreviations: CREA, creatinine; AST, aspartate transaminase; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; CRP, C reactive protein; CysC, cystatin C; PLT, platelet; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.