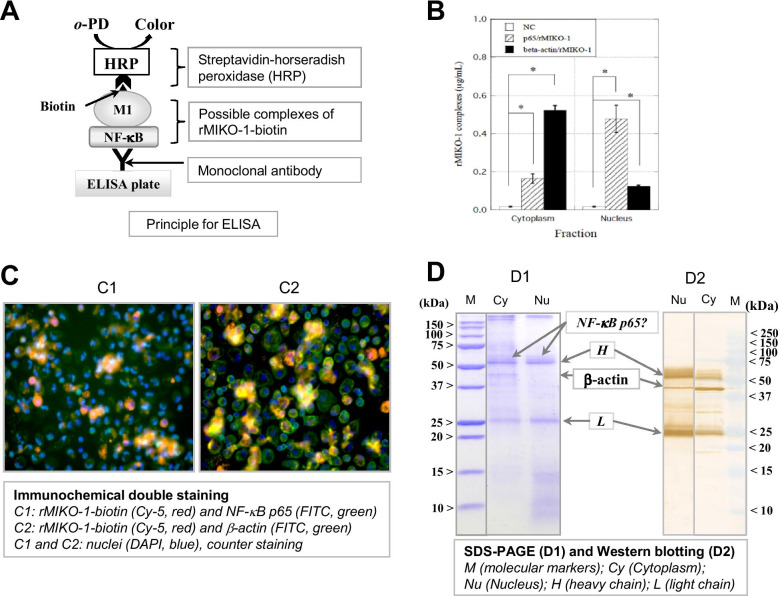
Fig. 6.
Possible complexes of rMIKO-1 with NF-κB p65 or β-actin in macrophages. (A) The principle of ELISA was schematically drawn in detail, in which M1, HRP, and o–PD indicate rMIKO-1, horseradish peroxidase, and o-phenylenediamine, respectively. (B) To detect the possible complex of rMIKO-1 with NF-κB p65 or β-actin, ELISA was performed using ELISA plates that were preliminarily coated with a specific antibody for NF-κB p65 or β-actin (5 μg/ml each) as the first antibody. rMIKO-1-biotin, a component of the complexes, was detected by the STA-HRP conjugate. HRP activity was assessed using o–PD and hydrogen peroxide as the substrates. (C) Fluorescent immunochemical double staining was performed using a specific monoclonal antibody for NF-κB p65 or β-actin (5 μg/ml) as the first antibody. Monoclonal antibodies and rMIKO-1-biotin were detected with anti-mouse IgG (horse)-FITC (secondary antibody, green) and STA-Cy5 (red) conjugates, respectively. C1: The colors of rMIKO-1, NF-κB p65, and the nucleus are red, green, and blue, respectively. C2: rMIKO-1 (red), β-actin (green), and the nucleus (blue). Microscopic images were shown using high power fields (×400). (D) SDS-PAGE and Western blotting were performed as previously described. Precipitated proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (D1). Proteins in the gel were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and Western blotting was performed using a specific monoclonal antibody for β-actin and the anti-mouse IgG (horse)-HRP conjugate as the first and second antibodies, respectively (D2), in which M indicates molecular markers. Cy and Nu indicate extracted protein fractions of the cytoplasm and nucleus, respectively, of macrophages. H and L indicate the heavy and light chains, respectively, of the first antibody. *, P<0.05.