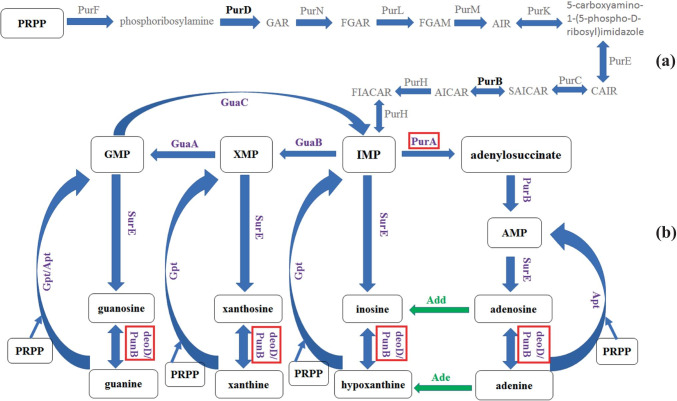
Fig. 1.
The purine nucleotide biosynthesis pathway in H. pylori. (a) De novo purine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway functioning in E. coli. Homologs for genes required for this pathway found in H. pylori are shown in black, while all enzymes for which homologs were not found in the H. pylori genome are marked in gray. (b) Purine salvage pathway in H. pylori; purine rings, shown in the bottom row, are obtained from environment. Enzymes that have been studied in H. pylori by mutant analysis and/or biochemistry are shown in violet. Enzymes described in this work, purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PunB, PNP) and adenylosuccinate synthetase (PurA, AdSS), are shown in red frames. Enzymes with likely function, but whose genes have not yet been identified are shown in green (figure adapted from Jenkins et al. 2011, Liechti and Goldberg 2012, Miller et al. 2012). Abbreviations: PRPP, 5-phosphoribosyl diphosphate; GAR, glycinamide ribonucleotide; FGAR, N-formylglycinamide ribonucleotide; FGAM, 5′-phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine; AIR, aminoimidazole ribotide; CAIR, 5′-phosphoribosyl-4-carboxy-5-aminoimidazole; SAICAR, 5′-phosphoribosyl-4-(N-succinocarboxamide)-5-aminoimidazole; AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribotide; FIACAR, 5′-phosphoribosyl-5-formamido-4-imidazolecarboxamide; PurF, amidophosphoribosyltransferase; PurD, phosphoribosylamine-glycine ligase; PurN, phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase; PurL, phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase; PurM, phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine cyclo-ligase; PurK, N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide synthase; PurE, N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide mutase; PurC, phosphoribosylaminoimidazole-succinocarboxamide synthase; PurH, bifunctional purine biosynthesis protein PurH; GuaB, IMP dehydrogenase; GuaA, GMP synthetase; GuaC, GMP reductase; PurA, adenylosuccinate synthetase; PurB, adenylosuccinate lyase; Gpt, hypoxanthine–guanine phosphoribosyl-transferase; Apt, adenine phosphoribosyltransferase; SurE, 5′-nucleotidase; PunB (deoD gene), purine nucleoside phosphorylase; Ade, adenine deaminase; Add, adenosine deaminase; IMP, inosine monophosphate; XMP, xanthosine monophosphate; GMP, guanosine monophosphate; AMP, adenosine monophosphate