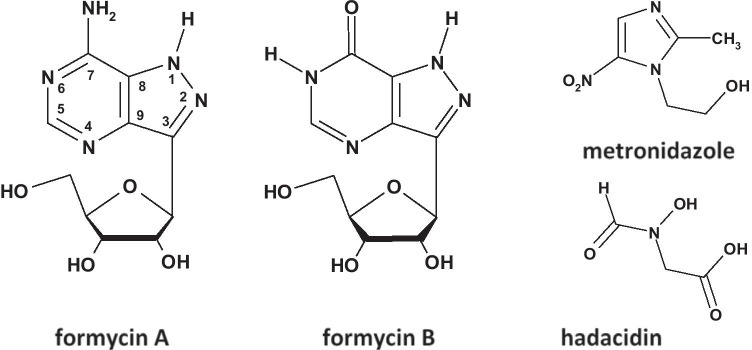
Fig. 2.
Inhibitors studied in this report, formycins A and B, hadacidin and metronidazole. Formycins A and B are structural analogues of natural PNP substrates, adenosine and inosine, respectively, with the C–C bond linking purine base and the sugar moiety, instead of the N–C glycosidic bond present in adenosine and inosine. Note the difference in base ring numbering of formycins when compared with purine ring numbering. In contrast to natural PNP substrates, adenosine, inosine, and guanosine, formycins may exist in more than one tautomeric form. Here the structure of N(1)-H tautomer is shown (Wierzchowski and Shugar 1982; Bzowska et al. 1992). Hadacidin is a structural analogue of one of the AdSS substrates, aspartate, and is a potent inhibitor of this enzyme (Iancu et al. 2006; Bubić et al. 2018). Metronidazole is an antibiotic efficiently used in therapy against H. pylori (e.g., Min Kim et al.; Olmedo et al. 2020), and it is used in this study as a positive control of the cellular uptake