Fig. 1.
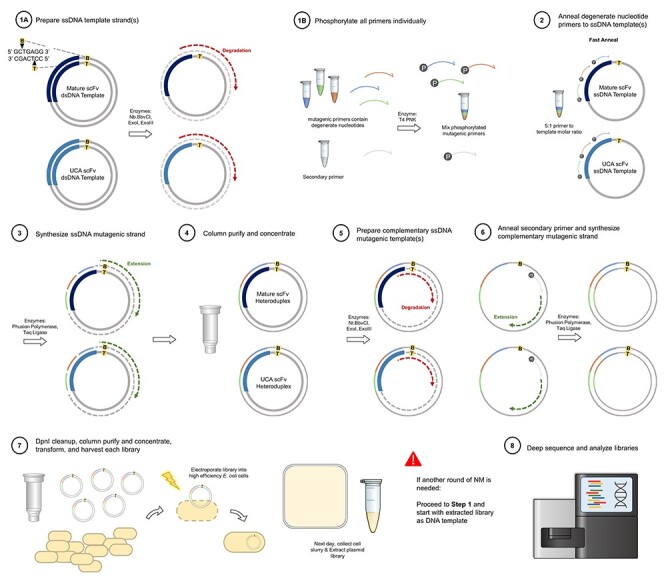
Combinatorial NM Flowchart. Steps 1A & 1B can be performed simultaneously and involve selectively nicking and degrading one strand of dsDNA parental template(s) (1A) and phosphorylating the degenerate nucleotide mutagenic primers and secondary primer (1B). Step 2: the phosphorylated mutagenic primers are annealed to the ssDNA parental template(s) using a fast annealing temperature program. Step 3: the remainder of the ssDNA mutagenic strand is synthesized and ligated. Step 4: the heteroduplex plasmid library is column purified and concentrated. Step 5: the complementary mutagenic strand is generated by selectively nicking and degrading the complementary strand of DNA. Step 6: the phosphorylated secondary primer is annealed to an unmutagenized region of the ssDNA template(s) and the remainder of the strand is synthesized and ligated. Step 7: an enzymatic DpnI cleanup step is followed by another column cleanup and concentration where the plasmid library is then ready for transformation and next-day harvest. At this point if another round of combinatorial NM is required, proceed to step 1 with the extracted library as the dsDNA template. Step 8: The library is deep sequenced and analyzed.
