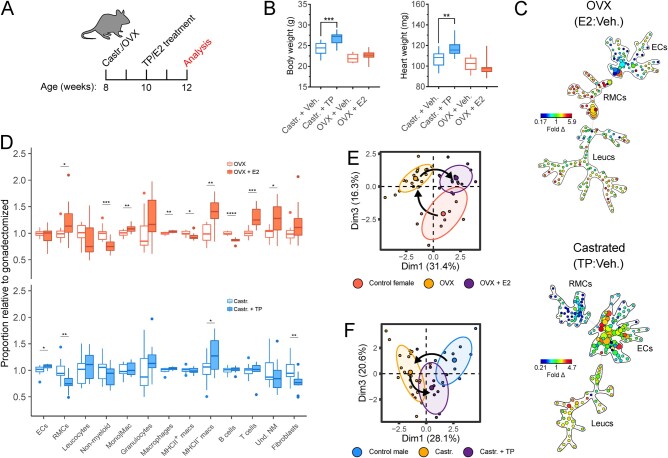
Figure 4.
Gonadal oestrogen and testosterone regulate cardiac resident mesenchymal levels (RMCs) and leucocyte subsets. (A) Experimental set-up for mouse OVX or Castr. followed by Veh. or TP/oestradiol (E2) treatment. (B) Body weight (left) and heart weight (right) measurements following gonadectomy with vehicle or TP/E2 treatment. (C) Ratiometric (TP: vehicle control and E2: vehicle control, Castr. males and OVX females, respectively) SPADE analysis of broad cardiac cell types. Heat map indicates fold difference (fold Δ) of cell populations in gonadectomized animals with TP or E2 treatment relative to gonadectomized animals with vehicle control treatment. (D) Relative abundance of broad cell types (ECs, RMCs, and Leucs), broad leucocyte subsets (non-myeloid, Mono|Mac., granulocytes), cardiac tissue macrophage subsets (MHCII+ macrophages and MHCII− macrophages) and non-myeloid subsets (B cells, T cells, and Und. NM cells) between gonadectomized animals treated with TP/E2 and gonadectomized animals treated with vehicle control. (E) Principal component analysis cellular composition of non-OVX (control), OVX, and OVX+E2 treatment cohorts. Arrows indicate movement of cellular composition signatures following ovariectomy and E2 treatment following ovariectomy. (F) Principal component analysis cellular composition of non-Castr. (control), Castr., and Castr.+TP treatment cohorts. Arrows indicate movement of cellular composition signatures following castration and TP treatment following castration. See Supplementary material online, Figure S3, for all flow cytometry gating parameters and markers used for SPADE clustering. n=10–12; all statistical analysis performed using Student’s t-test with statistical significance indicated as *(P≤0.05), **(P≤0.01), ***(P≤0.001), and ****(P≤0.0001). Whiskers of box and whisker plots represent the highest and the lowest values, except when a value is beyond the range of 1.5 inter-quartile.