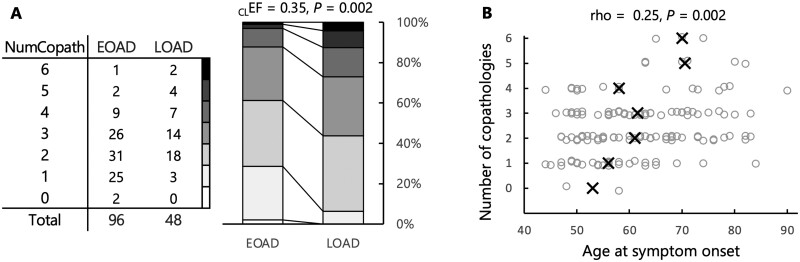
Figure 3.
Number of coexistent pathologies. (A) The table indicates the numbers of EOAD/LOAD patients with respective total number of co-pathologies, while the stacked bars illustrate the higher number of co-pathologies in the LOAD group. Mann-Whitney U-tests were conducted to compare the two groups; common language effect size [CLEF = U / (nEOAD × nLOAD)] represents the probability that a random value from the EOAD group is greater than a random value from the LOAD group. A Fisher’s exact test was also run to compare the proportion of co-pathology-free cases between the two groups. (B) Analyses conducted with age of onset as a continuous variable. Black crosses indicate the median ages for each level of co-pathology; a random jitter was applied on the y-axis to visualize all individual data-points.