Fig. 3.
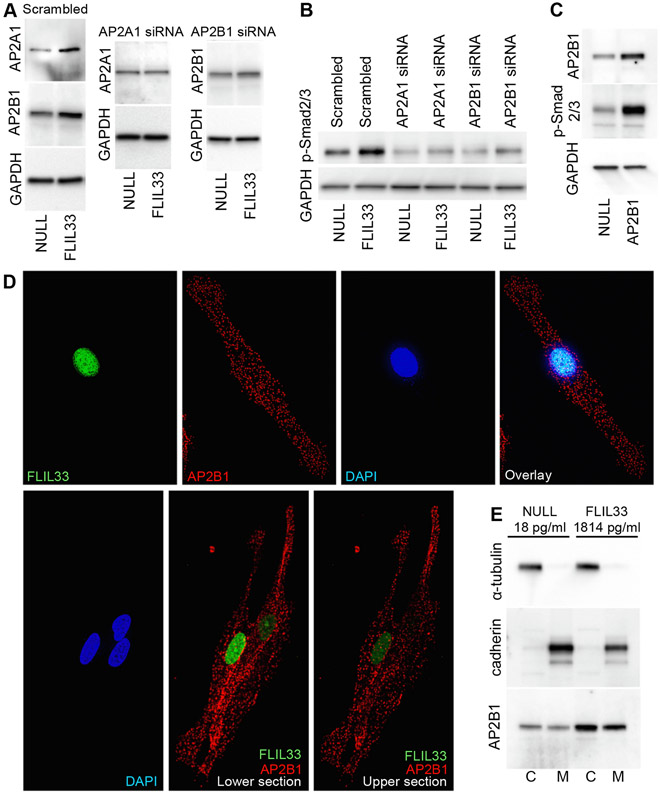
Subunits of the AP2 adaptor complex mediate the effect of elevated FLIL33 on Smad3 phosphorylation. A. Western blotting of NHLFs reveals that overexpression of FLIL33 elevates the levels of AP2A1 and AP2B1 subunits, and this effect is readily abrogated by specific indicated siRNAs but not scrambled siRNA. Repeated in three additional NHLF cultures from separate donors with similar results. B. AP2A1 or AP2B1 siRNAs, but not scrambled control siRNA, abrogate FLIL33 overexpression-induced Smad3 phosphorylation. Repeated in a separate NHLF culture from a different donor with similar results. C. Plasmid-mediated overexpression of AP2B1 is sufficient to induce Smad3 phosphorylation in the absence of FLIL33 overexpression. D. Fluorescence (top row) and optical sectioning (bottom row) microscopy of NHLFs overexpressing FLIL33mNG (green fluorescence) and immunostained for AP2B1 (red fluorescence); nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue fluorescence). In the bottom panel, the two shown subsections were 2 μm apart, showing that AP2B1 is not localized in the nucleus but is abundant on the cell surface and in the cytoplasm. Repeated in two additional NHLF cultures from separate donors, with similar results. E. Western blotting of cytoplasmic (C) and membrane (M) fractions of NHLFs transfected with the control NULL plasmid or FLIL33-encoding plasmid, as indicated. The indicated levels of IL-33 were measured by ELISA in total cell lysates.