Fig. 13. A suggested model of the modulatory function of MdWRKY75e in response to AAAP infection.
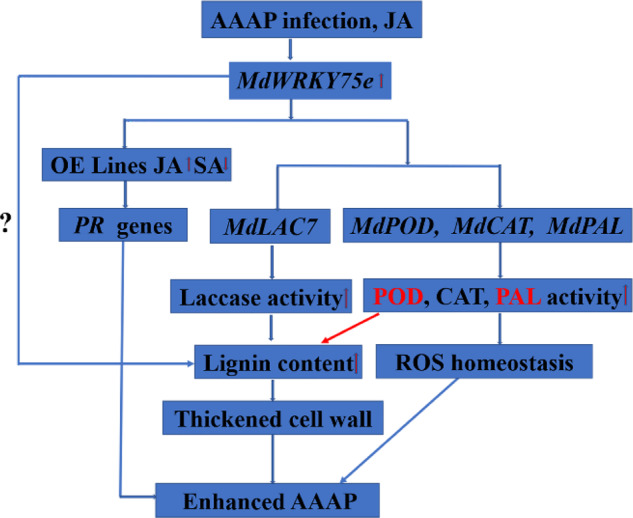
The JA signaling pathway is activated by AAAP (A. alternata apple pathotype) infection, resulting in increased expression levels of MdWRKY75e, which in turn modulates MdLAC7 by binding to W-box elements in its promoter. Upregulation of the MdWRKY75e–MdLAC7 interaction boosts laccase and lignin synthesis to strengthen mechanical defense capabilities, allowing AAAP infection-associated damage to be mitigated by sustaining ROS equilibrium and PR gene regulation
