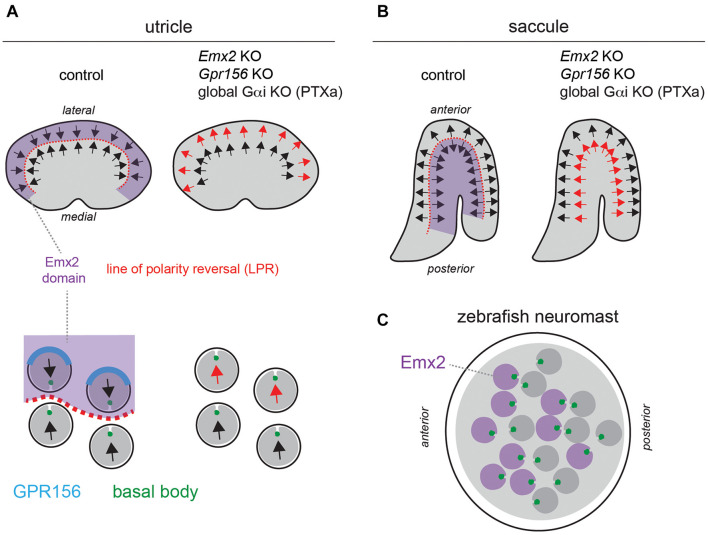
FIGURE 2.
A reversal in hair cell orientation occurs in the macular organs of the vestibular system and in fish neuromasts. (A,B) Diagram of HC orientation (arrows) and Emx2 regional expression (purple) in the mouse utricular (A) and saccular (B) maculae. A regional reversal in HC orientation in the Emx2-positive lateral utricle (A) and posterior saccule (B) creates a mirror-image organization at the organ level. This organization is lost in Emx2 and Gpr156 mutants, as well as upon Pertussis toxin (PTXa) expression. The bottom diagrams in panel (A) (utricle) show polarized enrichment of GPR156 (blue) at the lateral HC junction in Emx2-positive HCs above the line of polarity reversal (LPR, red), but not in Emx2-negative HCs below the LPR. (C) Diagram of an anterior-posterior neuromast in the larval zebrafish posterior lateral line. HCs expressing emx2 are indicated in purple. In all panels, arrows indicate HC orientation based on the position of the basal body/kinocilium (green), the shape of the hair bundle and other planar-asymmetric cytoskeletal elements.