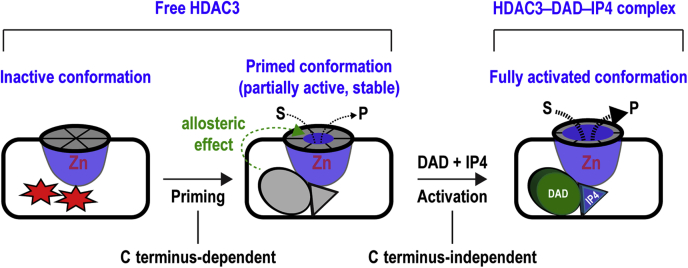
Figure 6.
A proposed model of the complete two-step HDAC3 activation pathway showing the different conformational states and cross talk between HDAC3 C terminus and DAD/IP4. HDAC3 activation requires two distinct steps that variably depend on the C terminus. First, the C terminus primes HDAC3 by stabilizing the DAD/IP4–binding sites and by allosterically enhancing the substrate accessibility, making HDAC3 partially active and poised for activation by DAD and IP4. Second, the primed HDAC3 is activated by DAD and IP4 in a C terminus–independent manner. In the left panel, the red-colored stars represent unstable conformations of the DAD and IP4-binding sites. These conformations were stabilized after priming, making them ready for binding by DAD and IP4. This is shown by the gray-colored ellipse and triangle in the middle panel that match the shapes of DAD and IP4, respectively, shown on the right. For simplicity, the C terminus was not shown in these representations. See text for details. DAD, deacetylase-activation domain; HDAC, histone deacetylase; IP4, inositol tetraphosphate.