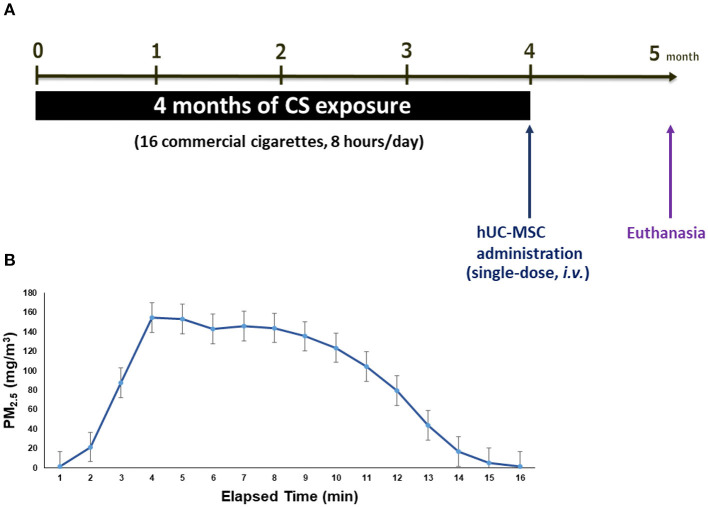
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic mice model of cigarette smoke (CS)-induced emphysema. (B) The distribution of particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of <2.5 μm (PM2.5) mass concentration in the whole-body exposure system (mean ± SD). Mice (8 weeks old, 20–25 g, n = 8–10 per group) were exposed to CS for 4 months and received (i.v.) a single dose of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) after CS exposure (CS + MSC-L: hUC-MSCs at 3 × 106 cells/kg body weight (BW) for low-dose, CS + MSC-M: 1 × 107 cells/kg BW for medium-dose, and CS + MSC-H: 3 × 107 cells/kg BW for high-dose).