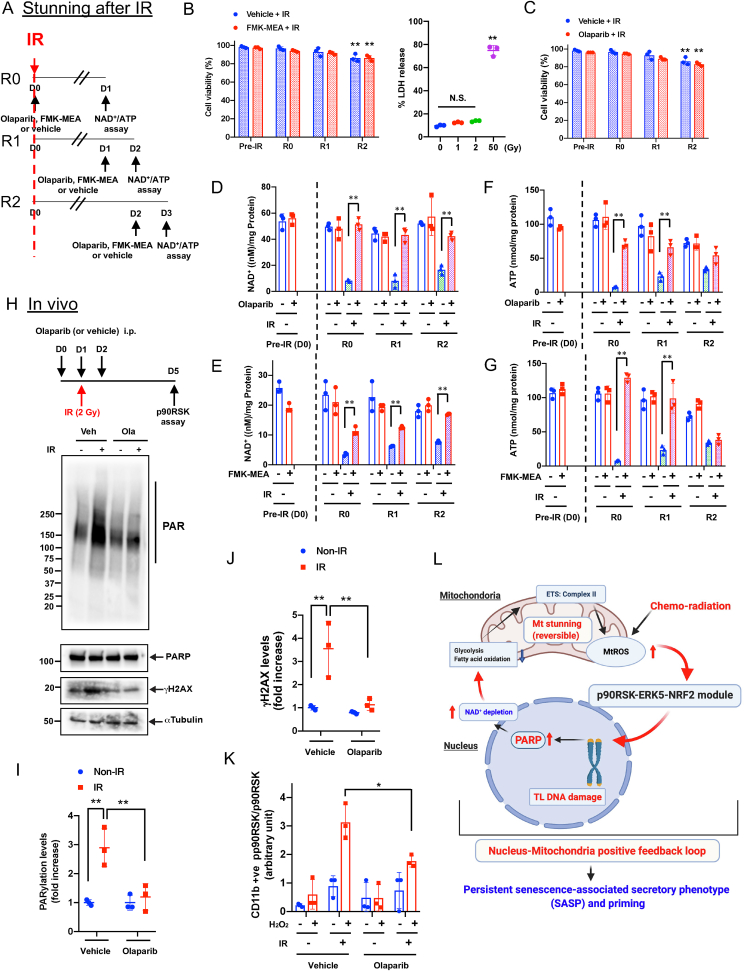
Fig. 7.
Roles of p90RSK and PARP activation in mitochondrial stunning, cell viability, DDR, and IR-induced priming.(A) A schema of how to detect mitochondrial stunning (recovery) after IR with PARP and p90RSK inhibitors. R0: On day 0 (D0), BMDMs from WT mice were pre-treated with the PARP inhibitor, olaparib (10 μM) or FMK-MEA (10 μM) for 1 h and then exposed to IR (2 Gy). One day (D1) after IR, NAD+ and ATP levels were measured. R1: BMDMs were exposed to IR and 1 day later, were treated with olaparib or FMK-MEA as in R0. After 2 days of IR (D2), NAD+ and ATP levels were measured. R2: WT BMDMs were exposed to IR and after 2 days, treated with olaparib or FMK-MEA as in R0. On day 3 (D3), NAD+ and ATP levels were measured. (B, C) BMDMs were treated with olaparib or FMK-MEA as described in A, and cell viability was measured by the Trypan blue-exclusion assay (B, left and C) and cell death by detecting LDH release into the culture medium. Mean ± SD, (n = 3). (D–G) BMDMs were treated with olaparib or FMK-MEA as in A, and NAD+ and ATP levels were measured as described in A. Mean ± SD, (n = 3). (H–K) Olaparib inhibited IR-induced monocyte priming. C57Bl/6 wild-type mice were treated with olaparib (10 mg/kg/day ip) from day (D) 0 to D2 and exposed to IR (2 Gy) on D1. On D5, PBMCs were isolated (top), and Western blotting was performed using the indicated antibodies (H). (I, J) The graphs represent PARylation and γH2AX densitometry data from 3 independent gels, one of which is shown in H (I: PARylation, J: γH2AX). (K) On D5, PBMCs were isolated as described in H (top), and p90RSK activity was measured in CD11b-positive cells before and after 10 min stimulation with H2O2 (200 μM). (L) A schematic showing the role of nucleus-mitochondria positive feedback loop mediated by the p90RSK activation-ERK5 S496 phosphorylation module and PARP activation in regulating mitochondrial stunning, priming, and consequent atherosclerosis. *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01. . (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)